Earth Observatory Water Cycle Overview

Viewed from space, one of the most striking features of our home planet is the water, in both liquid and frozen forms, that covers approximately 75% of the Earth’s surface. Geologic evidence suggests that large amounts of water have likely flowed on Earth for the past 3.8 billion years—most of its existence. Believed to have initially arrived on the surface through the emissions of ancient volcanoes, water is a vital substance that sets the Earth apart from the rest of the planets in our solar system. In particular, water appears to be a necessary ingredient for the development and nourishment of life.
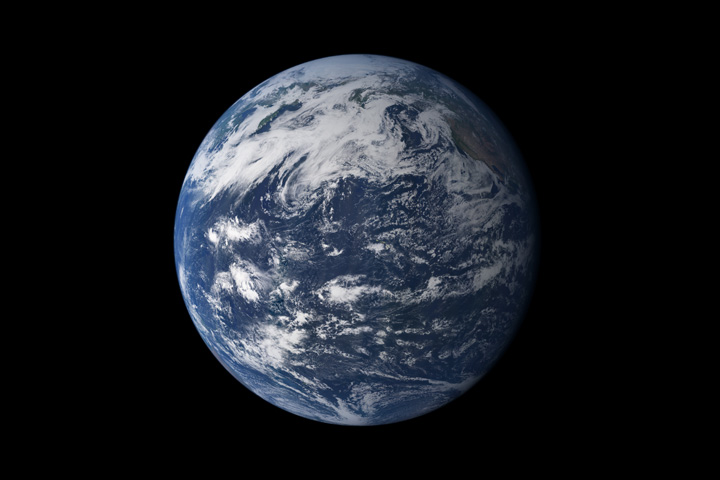 Earth is a water planet: three-quarters of the surface is covered by water, and water-rich clouds fill the sky. (NASA.)
Earth is a water planet: three-quarters of the surface is covered by water, and water-rich clouds fill the sky. (NASA.)
Water, Water, Everywhere
Water is practically everywhere on Earth. Moreover, it is the only known substance that can naturally exist as a gas, a liquid, and solid within the relatively small range of air temperatures and pressures found at the Earth’s surface.
 Water is the only common substance that can exist naturally as a gas, liquid, or solid at the relatively small range of temperatures and pressures found on the Earth’s surface. Sometimes, all three states are even present in the same time and place, such as this wintertime eruption of a geyser in Yellowstone National Park. (Photograph ©2008 haglundc.)
Water is the only common substance that can exist naturally as a gas, liquid, or solid at the relatively small range of temperatures and pressures found on the Earth’s surface. Sometimes, all three states are even present in the same time and place, such as this wintertime eruption of a geyser in Yellowstone National Park. (Photograph ©2008 haglundc.)In all, the Earth’s water content is about 1.39 billion cubic kilometers (331 million cubic miles), with the bulk of it, about 96.5%, being in the global oceans. As for the rest, approximately 1.7% is stored in the polar icecaps, glaciers, and permanent snow, and another 1.7% is stored in groundwater, lakes, rivers, streams, and soil. Only a thousandth of 1% of the water on Earth exists as water vapor in the atmosphere.
Despite its small amount, this water vapor has a huge influence on the planet. Water vapor is a powerful greenhouse gas, and it is a major driver of the Earth’s weather and climate as it travels around the globe, transporting latent heat with it. Latent heat is heat obtained by water molecules as they transition from liquid or solid to vapor; the heat is released when the molecules condense from vapor back to liquid or solid form, creating cloud droplets and various forms of precipitation.
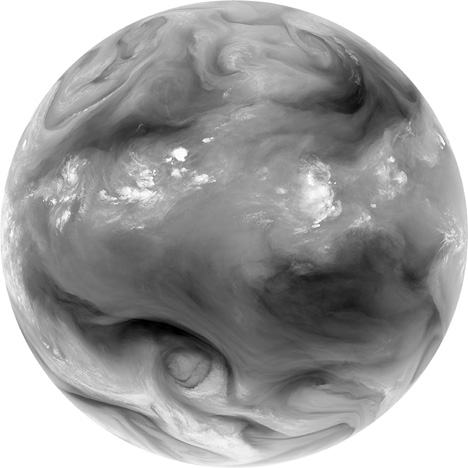 Water vapor—and with it energy—is carried around the globe by weather systems. This satellite image shows the distribution of water vapor over Africa and the Atlantic Ocean. White areas have high concentrations of water vapor, while dark regions are relatively dry. The brightest white areas are towering thunderclouds. The image was acquired on the morning of September 2, 2010 by SEVIRI aboard METEOSAT-9. [Watch this animation (23 MB QuickTime) of similar data to see the movement of water vapor over time.] (Image ©2010 EUMETSAT.)
Water vapor—and with it energy—is carried around the globe by weather systems. This satellite image shows the distribution of water vapor over Africa and the Atlantic Ocean. White areas have high concentrations of water vapor, while dark regions are relatively dry. The brightest white areas are towering thunderclouds. The image was acquired on the morning of September 2, 2010 by SEVIRI aboard METEOSAT-9. [Watch this animation (23 MB QuickTime) of similar data to see the movement of water vapor over time.] (Image ©2010 EUMETSAT.)
| Estimate of Global Water Distribution | Volume (1000 km3) | Percent of Total Water | Percent of Fresh Water |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oceans, Seas, and Bays | 1,338,000 | 96.5 | - |
| Ice Caps, Glaciers, and Permanent Snow | 24,064 | 1.74 | 68.7 |
| Groundwater | 23,400 | 1.7 | - |
| Fresh | (10,530) | (0.76) | 30.1 |
| Saline | (12,870) | (0.94) | - |
| Soil Moisture | 16.5 | 0.001 | 0.05 |
| Ground Ice and Permafrost | 300 | 0.022 | 0.86 |
| Lakes | 176.4 | 0.013 | - |
| Fresh | (91.0) | (0.007) | .26 |
| Saline | (85.4) | (0.006) | - |
| Atmosphere | 12.9 | 0.001 | 0.04 |
| Swamp Water | 11.47 | 0.0008 | 0.03 |
| Rivers | 2.12 | 0.0002 | 0.006 |
| Biological Water | 1.12 | 0.0001 | 0.003 |
| Total | 1,385,984 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Source: Gleick, P. H., 1996: Water resources. In Encyclopedia of Climate and Weather, ed. by S. H. Schneider, Oxford University Press, New York, vol. 2, pp.817-823. | |||
For human needs, the amount of freshwater on Earth—for drinking and agriculture—is particularly important. Freshwater exists in lakes, rivers, groundwater, and frozen as snow and ice. Estimates of groundwater are particularly difficult to make, and they vary widely. (The value in the above table is near the high end of the range.)
Groundwater may constitute anywhere from approximately 22 to 30% of fresh water, with ice (including ice caps, glaciers, permanent snow, ground ice, and permafrost) accounting for most of the remaining 78 to 70%.

