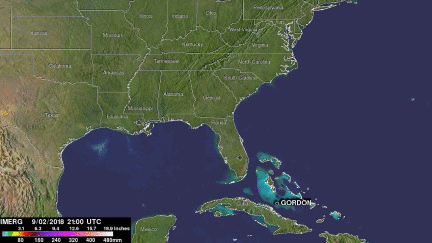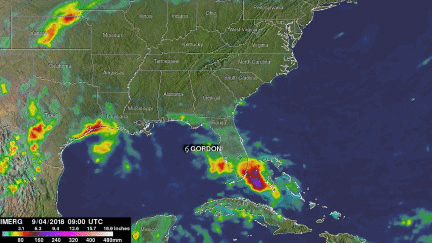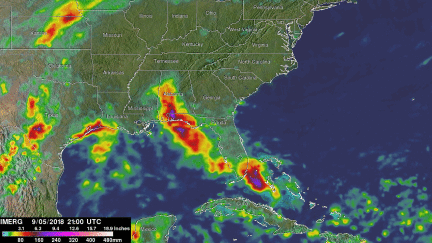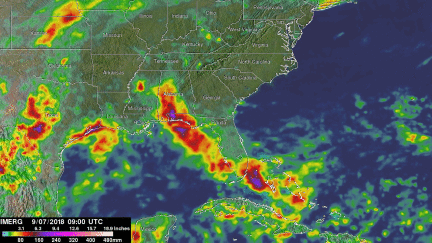
Tropical Storm Gordon's Rainfall Measured With IMERG
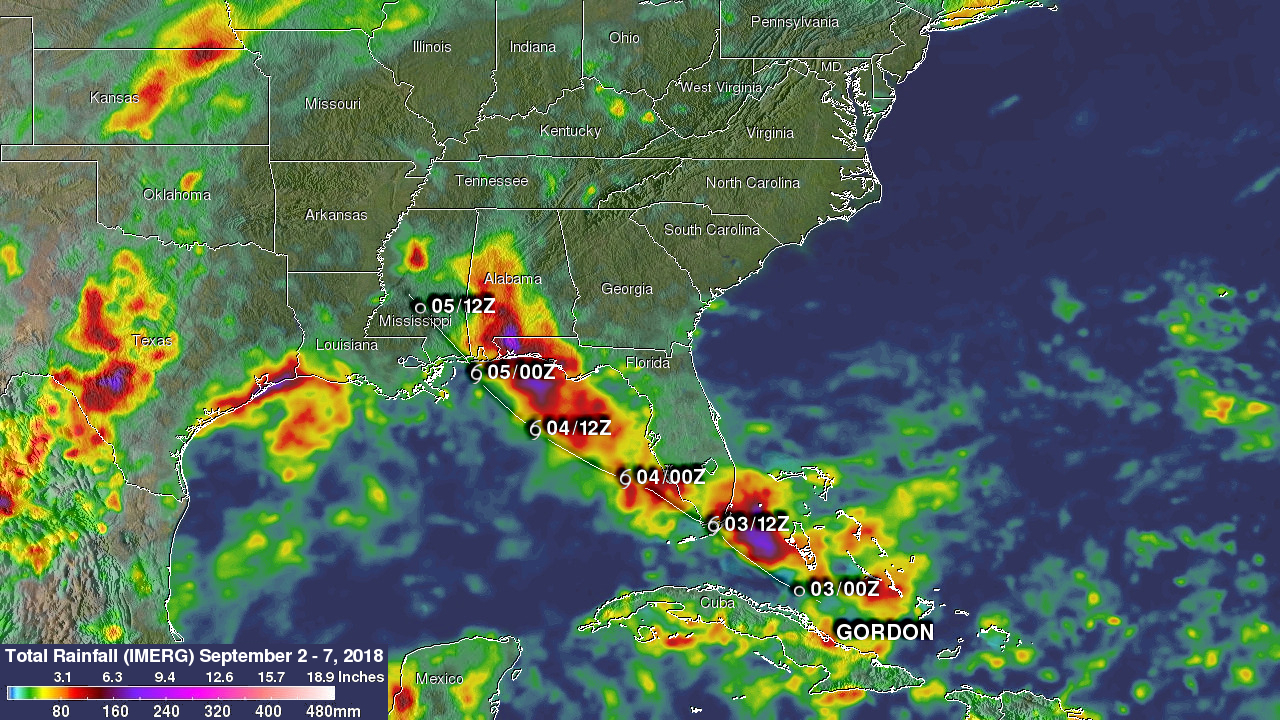
Tropical Storm Gordon became the seventh named system of the 2018 Atlantic hurricane season on Monday September 3, 2018. GORDON became more intense as it moved through the eastern Gulf Of Mexico but didn't quite make it to hurricane force before landfall. GORDON was a strong tropical storm with winds of about 70 mph (~ 61 kts) when it hit southeastern Mississippi on September 5, 2018. GORDON continued to produce rainfall as it moved inland. Weakening GORDON spawned a tornado near Picayune, Mississippi on Thursday September 6, 2018. Today, tropical depression GORDON is still responsible for flash flood Watches for parts of Arkansas, Missouri and the lower Ohio Valley.
NASA's Integrated Multi-satellitE Retrievals for GPM (IMERG) data were used to estimate the total amount of rain that tropical storm GORDON dropped from September 2 to early September 7, 2018. During that period tropical storm GORDON dropped heavy rain along it’s path through the western Bahamas, southern Florida, Alabama and Mississippi. This IMERG analysis also shows that during this period heavy precipitation fell along the Gulf Coasts of Texas and southwestern Louisiana. That heavy rainfall was due to a separate low pressure center that moved through the northwestern Gulf Of Mexico. IMERG data indicated that tropical storm GORDON dropped the most extreme rainfall over Mississippi, Alabama and the Florida Panhandle. IMERG estimates indicated that rainfall totals were greater than 10.0 inches (254 mm) in those areas.
The remnants of GORDON are expected to move occasionally heavy rain into the Ohio valley over the weekend.