Using GPM Data for Water Resources, Agricultural Forecasting & Food Security
Growing human population, increased demand for water and energy, and a changing climate have contributed to concerns of how freshwater resources and food supply and production may be stressed. Both water resource managers and the agricultural community need to know the amount, distribution, timing and onset of seasonal rain and snow to prepare for freshwater shortages and forecast crop yields. Remotely sensed precipitation estimates play a key role in predicting changes in freshwater supply and agricultural forecasting. Specifically, GPM provides advance precipitation measurements on regional and global scales frequently, which allows for a better understanding of precipitation systems, water cycle variability, and freshwater availability. The Water Resources, Agricultural Forecasting and Food Security applications area encourages the use of GPM precipitation data to analyze and forecast changes that affect water resources and its subsequent impact on agricultural productivity.
Overview
Growing human population, increased demand for water and energy, and a changing climate have contributed to concerns of how freshwater resources, food supply and production may be stressed. Both water resource managers and the agricultural community need to know the amount, distribution, timing and onset of seasonal rain and snow to prepare for freshwater shortages and forecast crop yields. Remotely sensed precipitation estimates play a key role in predicting changes in freshwater supply and agricultural yields. Specifically, GPM provides advanced, frequent precipitation measurements on regional and global scales, which allows for a better understanding of precipitation systems that affect water cycle and freshwater availability. The Water and Agricultural applications area highlights the use of GPM precipitation data in applications related to water resources and its impact on agricultural productivity.
GPM Data for Decision Making
USAID works to protect river and watershed ecosystems to ensure adequate water quality and a healthy habit to support biodiversity. Credit: Richard Volk/USAID
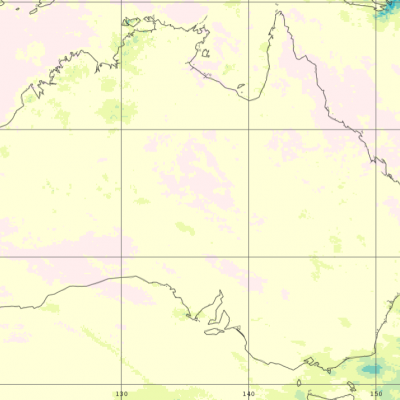
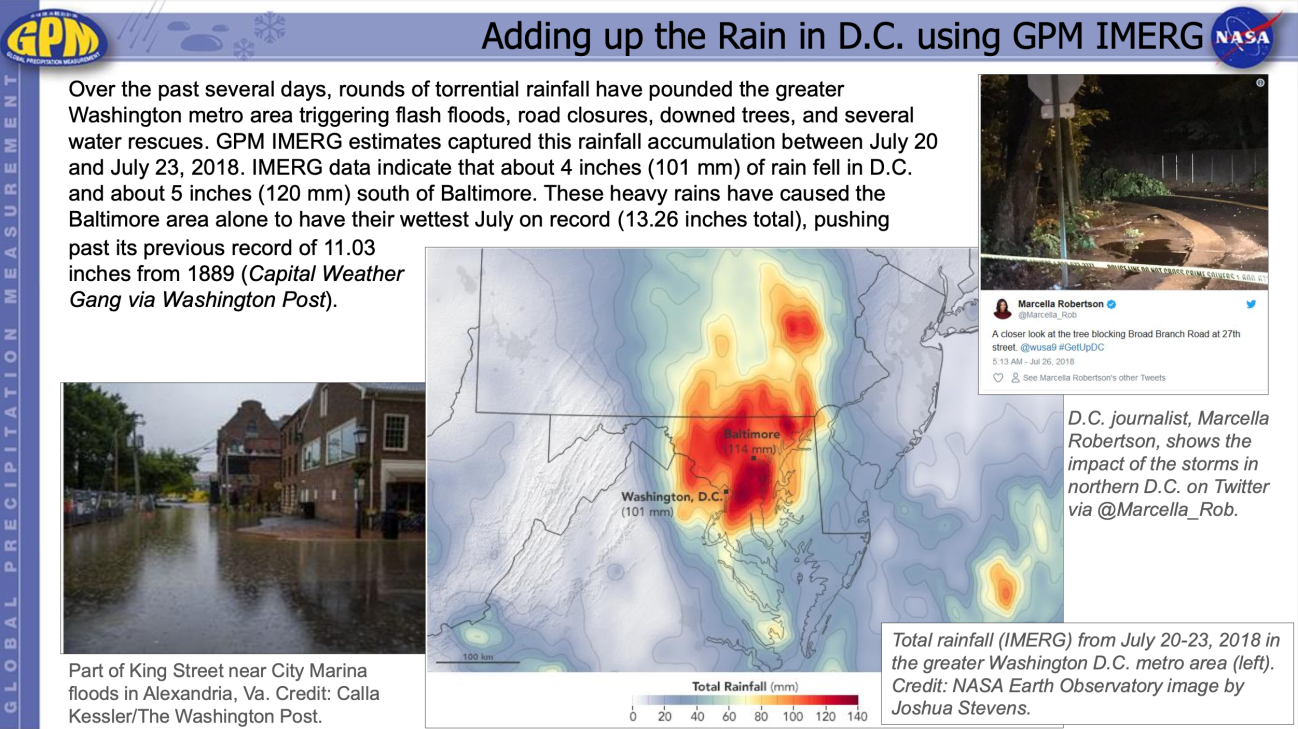
Water resource managers rely on accurate precipitation measurements to monitor freshwater resources necessary for human activities including public consumption, irrigation, sanitation, mining, livestock and powering industries. GPM provides useful rainfall estimates at regional and global scales as well as frequently to help scientists understand droughts and consequent freshwater availability. Global observation of precipitation from the GPM constellation of satellites will allow scientists to better understand and predict changes in freshwater supply.
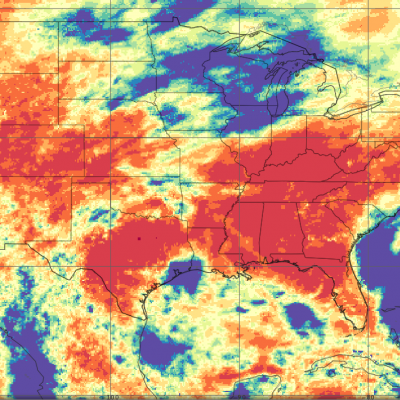
Remotely sensed precipitation estimates play a key role in monitoring and modeling efforts for organizations and companies that track food and water security. In addition to the amount and distribution of seasonal rainfall, the timing of the onset of rainfall is an important variable for early estimation of growing season outcomes like crop yield. With their global coverage, satellites can also observe the results of natural disasters such as droughts, floods, and persistent or deficient snow cover that can affect agricultural productivity. In particular, satellite precipitation estimates from GPM, combined with other environmental datasets, are used to determine the extent and availability of surface rainfall over farm and ranchland. These estimates are then used within agricultural forecast models to analyze and predict crop yield.
SERCH LIGHTS tools can give soybean producers the heads up about drought. Credit: USDA photo by Bob Nichols
Climate and weather are significant factors affecting agriculture production around the world. The correlation between crop volumes and weather can result in a successful yield or a financial disaster. As a result, farmers need to be increasingly efficient in their water management practices. GPM precipitation estimates are used by private companies to define extreme precipitation thresholds to support microinsurance, providing farmers with protection against loss of or damage to crops and/or livestock.
Water & Agriculture Featured Resources
Unexpected shocks from natural hazards can affect populations throughout the globe, threatening sustainable development and resilience. However, the impacts of these events, such as extreme precipitation or drought, disproportionately affect the developing world where individuals often are not insured and live and work in conditions that leave them vulnerable to natural disasters. This can lead to significant economic and environmental challenges if preventive measures or mitigating measures are not taken in time. To reduce risks from natural disasters and build climate resilience, decision...
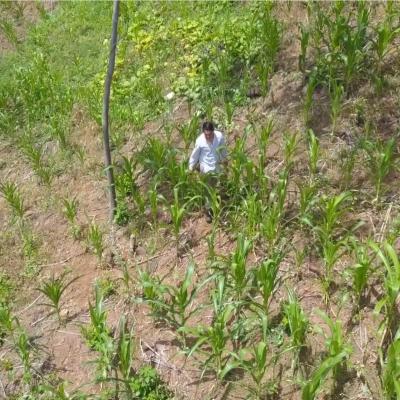
Agriculture in Pakistan is dependent on irrigation from the Indus River. But over the years, these freshwater resources have become scarce. Today, it is one of the world’s most depleted basins. To tackle this, farmers are attempting to predict and track freshwater resources with the help of NASA satellites and cell phones.
This video is public domain and along with other supporting visualizations can be downloaded from NASA Goddard's Scientific Visualization Studio at: https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/13592
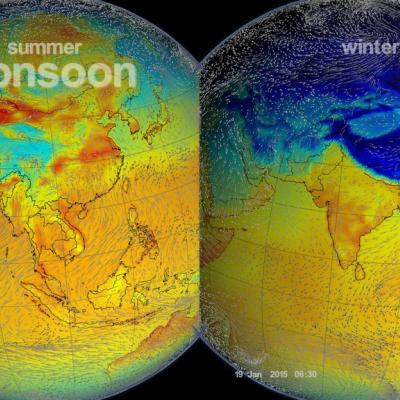
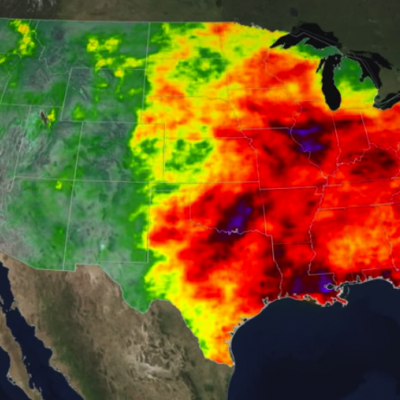
North America experiences a yearly monsoon weather system in late summer as moisture comes up from the west coast of Mexico and enters the southwestern U.S. The seasonal weather pattern brings both much of the region's precipitation but can also pose a threat in the form of flash flooding. The Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) mission gathers data from these storms in order to better understand the precipitation processes happening within, which can help better forecast the breaks and surges in the monsoon.
- GPM Water & Agricultural Applications One-pager (pdf)
- Applied Remote Sensing Training (ARSET) for Water Resources
- Goddard Applied Sciences Water Applications Working Group
- NASA Food Security Initiative
- NASA Applied Sciences Program Water Resources Applications
- Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) Mission