science
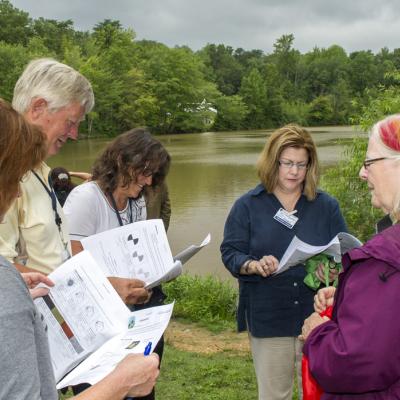
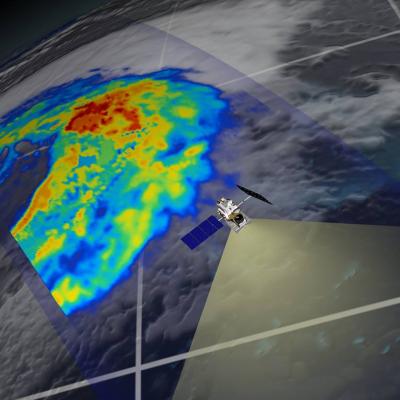
The Global Precipitation Measurement mission Core Observatory is performing normally. The GPM Microwave Imager (GMI) continues in science mode, and GMI data is being sent to the Precipitation Processing System (PPS) at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. Using the initial data, the instrument team has verified that GMI is working well on-orbit. The GPM Core Observatory will have a 60 day on-orbit check out period to ensure the healthy operation of the spacecraft and instruments. Precipitation data will be released from the PPS no later than 6 months post-launch, after the
GPM Science Briefing
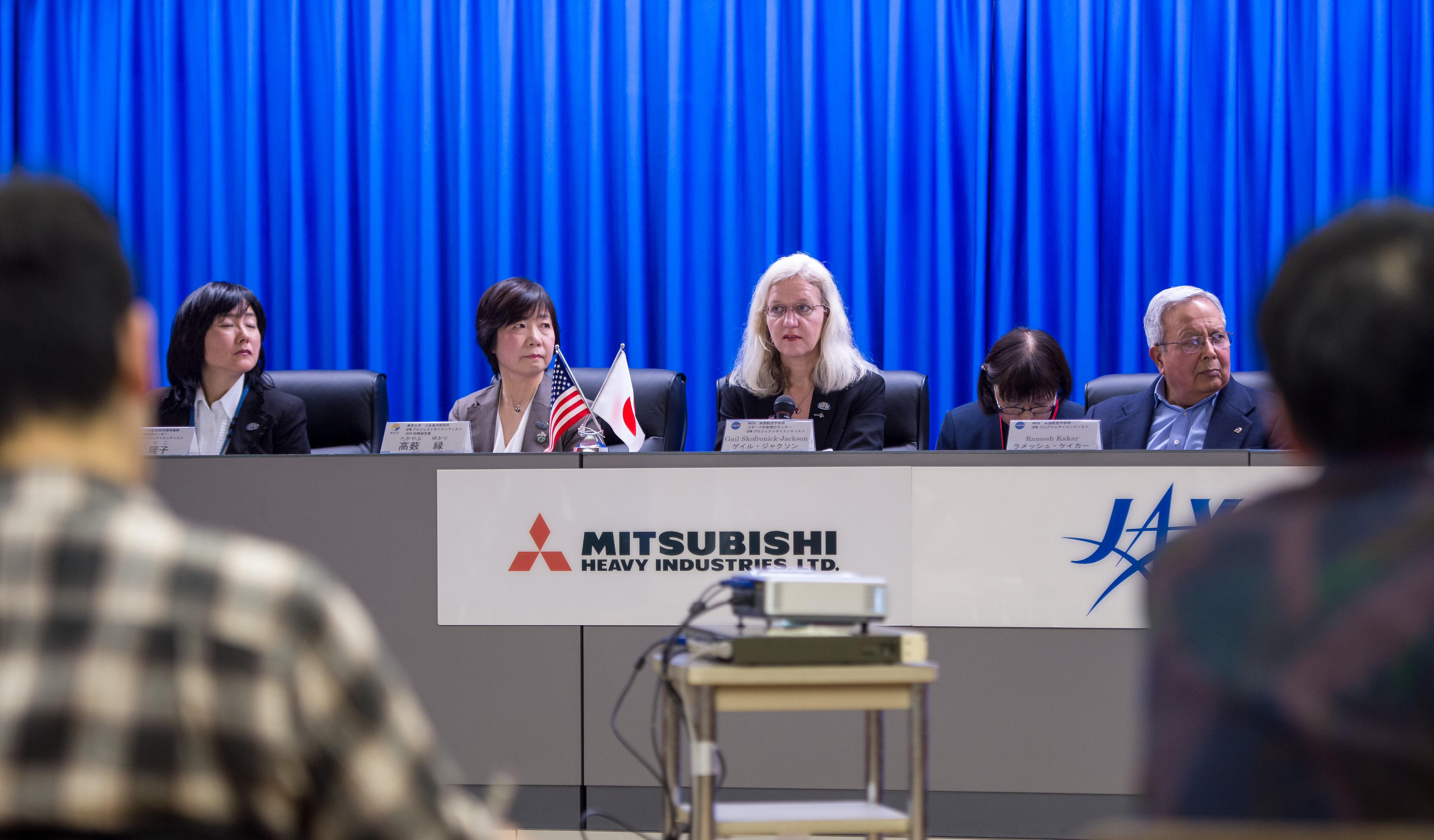

Image Caption
GPM Science Briefing
From left: Riko Oki, GPM Project Scientist, JAXA, Yukari Takayabu, Professor, Atmosphere and Ocean Research Institute, Gail Skofronick-Jackson, NASA GPM Project Scientist, and, Ramesh Kakar, GPM Program Earth Scientist , NASA Headquarters, are seen during a science briefing for the launch of the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory aboard an H-IIA rocket, Wednesday, Feb. 26, 2014, Tanegashima Space Center, Japan. Launch is scheduled for early in the morning of Feb. 28 Japan time.