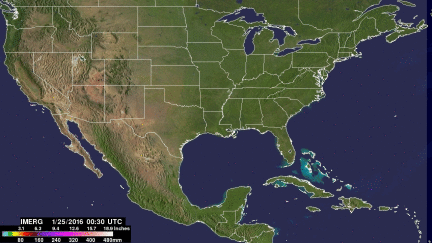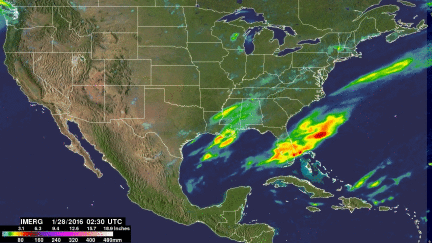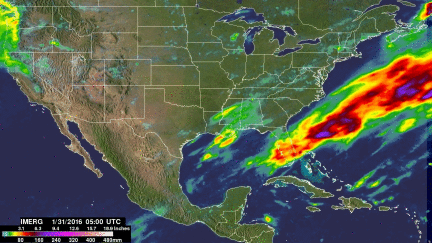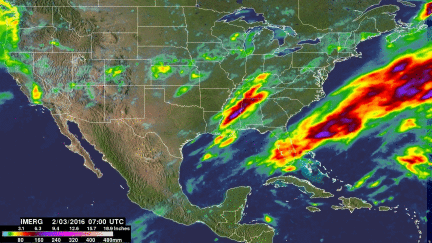
Extreme Precipitation Measured From Space
For over a week the weather over the continental United State's has been punctuated by extreme events. Automobiles were thrown around on January 27, 2016 by tornadoes that hit southern Florida. On January 31 a winter storm with heavy rain, strong winds and isolated thunderstorms hit southern California killing at least one person. There were numerous reports of hail with these storms ranging from pea sized to up to an inch in diameter. Powerful winds with these storms also brought down trees and power lines. A blizzard that followed the Democratic and Republican caucuses in Iowa dropped over 18 inches of snow in the Great Plains. Eleven tornadoes, spawned from a supercell thunderstorm, were reported On Tuesday February 2, 2016 in Mississippi and Alabama.
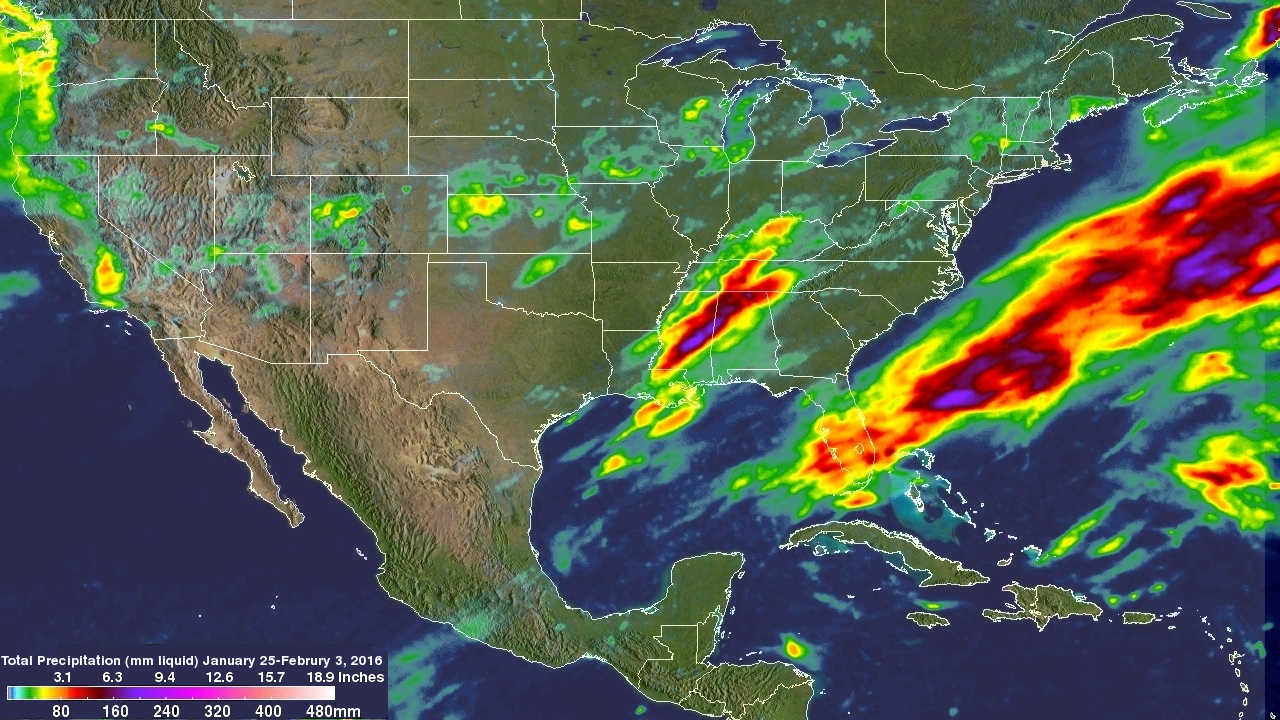
Precipitation that occurred during the period from January 25 though the early hours of February 3, 2016 was estimated by NASA's Integrated Multi-satellite Retrievals for the Global Precipitation Measurement mission (IMERG). Precipitation estimates are shown as liquid water although snowfall depths can be up to ten times greater. The most extreme precipitation over the United States during this period was estimated by IMERG to be over 200mm (7.9 inches) in an area where stormy weather frequently hit Mississippi and Alabama.
Due to the current strong El Nino, extreme precipitation events are expected to continue through the winter.