2011 a Wet Spring for the Central US
A combination of heavy rains and a large snow melt has put parts of the central US at risk for record flooding this spring with several locations along the Mississippi already at or near record levels. One likely culprit is La Nina. Despite the fact that the current La Nina appears to be winding down, it's effects in the atmosphere can persist for a while. Furthermore, although not every La Nina brings major flooding to the region, La Nina's are conducive for above-normal rainfall from East Texas and northern Louisiana up through Arkansas and the Tennessee and Ohio Valleys with below-normal rainfall across Texas, southern Louisiana and Florida. During La Nina, below-normal sea surface temperatures occur in the equatorial East Pacific and above-normal temperatures in the West Pacific. This pattern leads to enhanced tropical thunderstorm activity over the West Pacific, which in turn can influence the weather in middle latitudes by shifting the jet stream pattern. On average, La Nina's favor an upper-level trough over the Midwest with the jet steam dipping down out of the northern Rockies and flowing west-to-east across the central Mississippi and Ohio Valleys before heading back up over the Northeast. This pattern steers developing low pressure systems across the Plains and central Mississippi into the Tennessee and Ohio Valleys. These areas of low pressure provide the focus for showers and storms while drawing warm moist air up from the Gulf of Mexico, resulting in enhanced rainfall across the central part of the country.
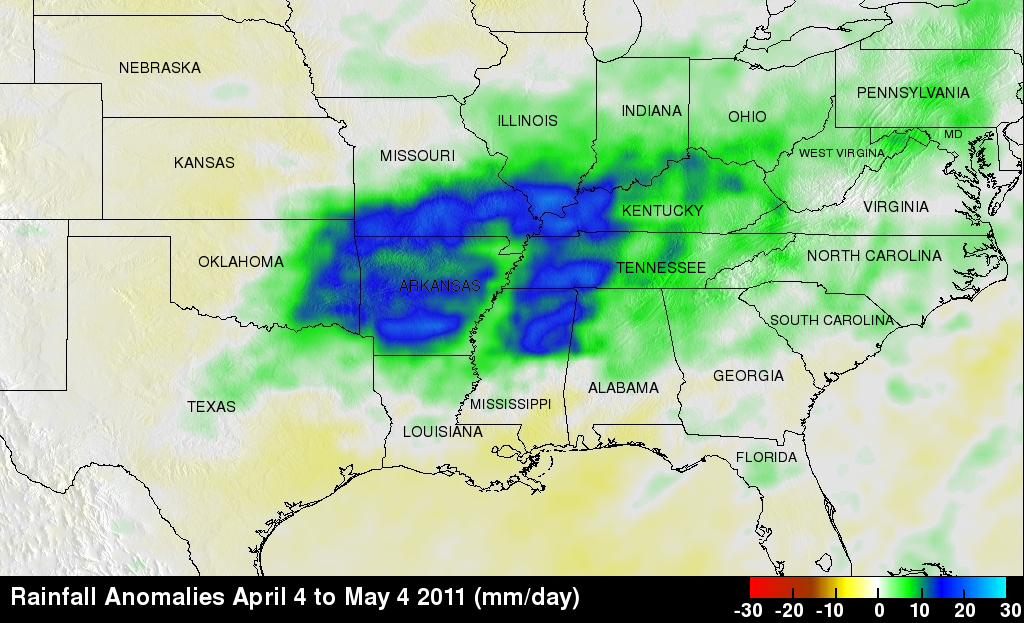
The main objective of the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite is to measure rainfall over the global Tropics. TRMM measures rainfall using a combination of passive microwave and active radar sensors. For expanded coverage, TRMM can be used to calibrate rainfall estimates from other satellites. The TRMM- based, near-real time Multi-satellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA) at the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center provides rainfall estimates over the global Tropics. TMPA rainfall anomalies are shown here for the period 4 April to 4 May 2011 for the eastern two thirds of the country. The anomalies were constructed by computing the average rainfall rate over the period and then subtracting the 10-year average rate for the same period. The resulting pattern shows a broad area of above-normal rainfall (shown in green and blue) stretching from eastern Oklahoma across the central Mississippi Valley and up into the lower Ohio Valley with below-normal rainfall along the northern Gulf Coast. This rainfall pattern is consistent with a La Nina.
In addition to rainfall, this type of jet stream pattern can lead to strong storms by allowing strong jet stream winds to override warm moist air from the Gulf as was evidenced by the recent tornado outbreak. In fact, some of the biggest tornado outbreaks, including the previous record "Super Outbreak" in 1974, have occurred during La Nina's.
Image by Hal Pierce (SSAI/NASA GSFC) and Caption by Steve Lang(SSAI/NASA GSFC)