GPM Flies Over Hurricane Gonzalo
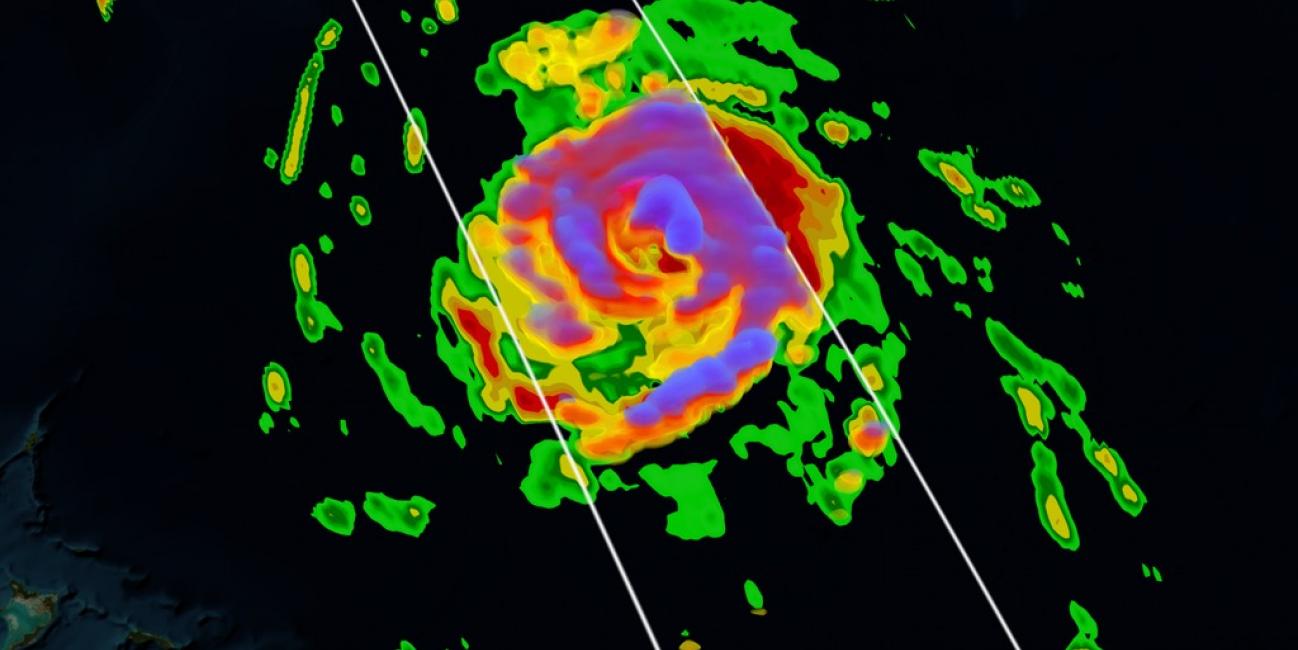
On October 16th, 2014 (1342 UTC) the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) mission's Core Observatory flew over Hurricane Gonzalo as it headed towards Bermuda. Hurricane Gonzalo remains a category 4 hurricane on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale, with maximum sustained winds at 130 mph. As of 12:00 UTC (8:00a.m. EDT) on Friday, October 17th, the National Hurricane Center forecast located the storm about 195 miles south southwest of Bermuda, where a hurricane warning is in effect.
The GPM Core Observatory carries two instruments that show the location and intensity of rain and snow, which defines a crucial part of the storm structure – and how it will behave. The GPM Microwave Imager sees through the tops of clouds to observe how much and where precipitation occurs. The Dual-frequency Precipitation Radar provides the three-dimensional view, showing the structure of the storm spiraling inward toward the center, with heavier rain on the north side of the storm. Shades of blue represent ice in the upper part of clouds. Viewed from the side, the stark color change from blue to green marks the transition from ice to rain.
For forecasters, GPM's microwave and radar data are part of the toolbox of satellite data, including other low Earth orbit and geostationary satellites, that they use to monitor tropical cyclones and hurricanes.
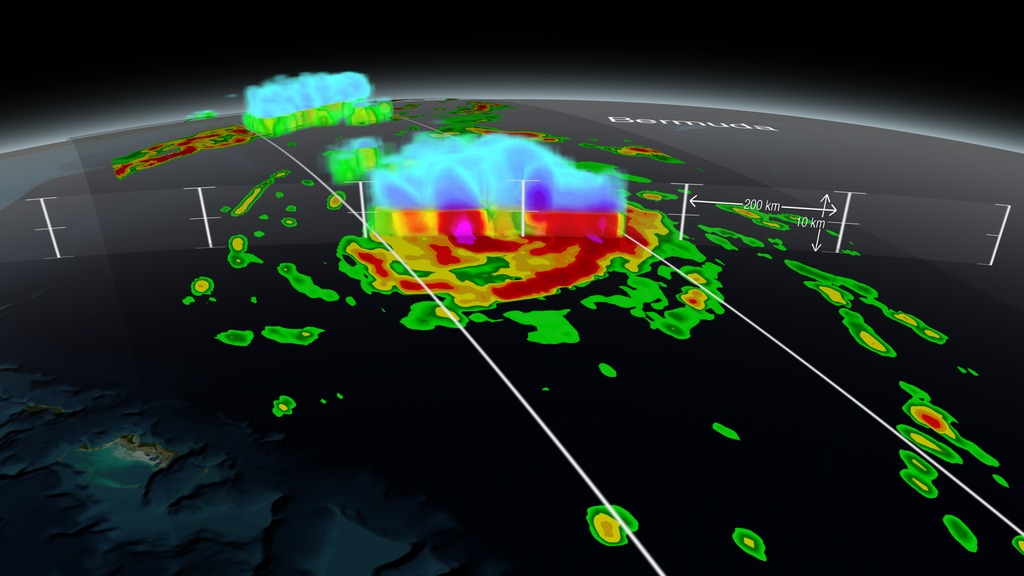 Hurricane Gonzalo being scanned through the center of the DPR data showing the inner volumetric rain rates.
Hurricane Gonzalo being scanned through the center of the DPR data showing the inner volumetric rain rates.The addition of GPM data to the current suite of satellite data is timely. Its predecessor precipitation satellite, the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission, is 18 years into what was originally a three-year mission. GPM's new high-resolution microwave imager data and the unique radar data ensure that forecasters and modelers won't have a gap in coverage. GPM is a joint mission between NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency. All GPM data products can be found at NASA Goddard's Precipitation Processing Center website: http://pps.gsfc.nasa.gov
High Resolution downloadable video available at SVS: https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/4230