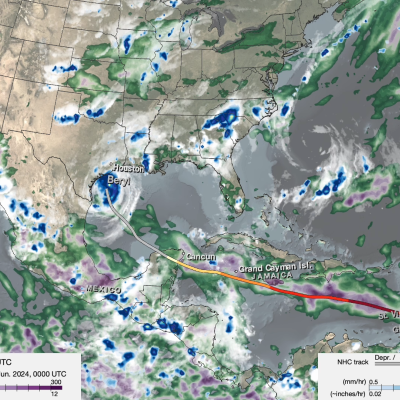
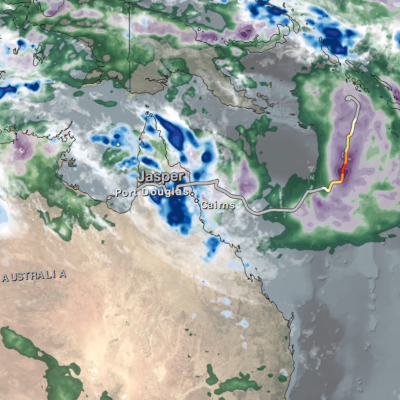
Tropical Cyclones
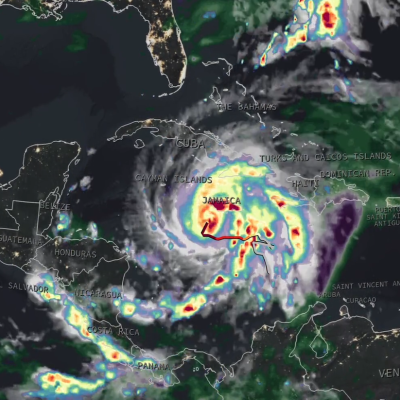
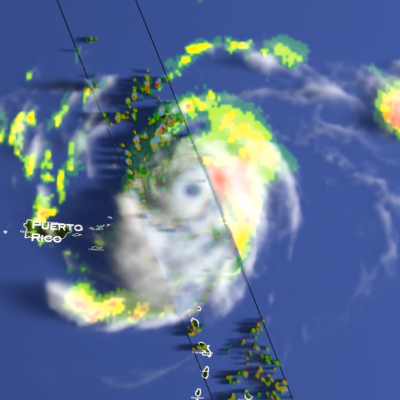
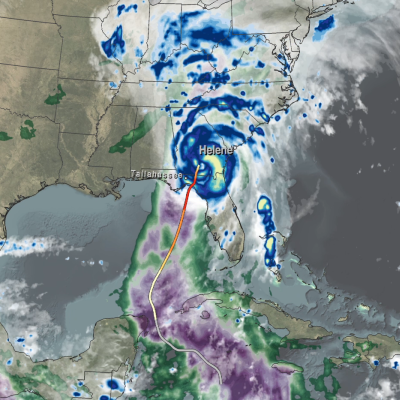
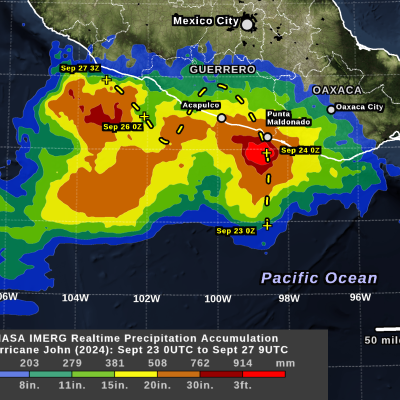
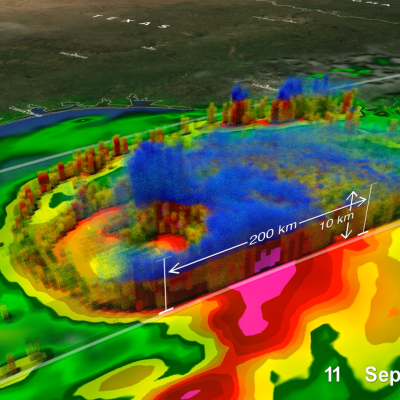
The GPM Mission provides insight into how and why some tropical cyclones intensify and others weaken as they move from tropical to mid-latitude systems. The GPM Core Observatory’s GMI and DPR instruments allow scientists to study the internal structure of storms throughout their life cycle, and view how they change over time.