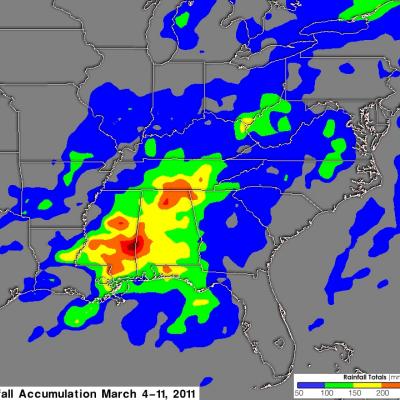
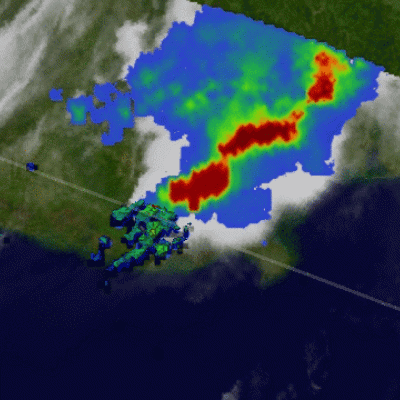
TRMM Sees Strong Thunderstorms in ARANI
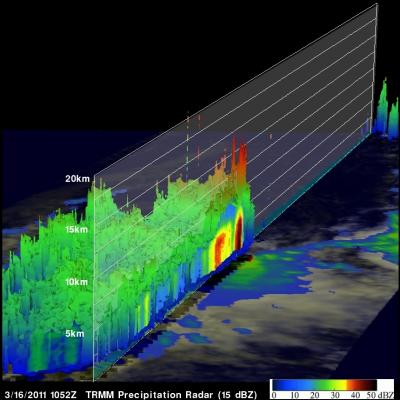
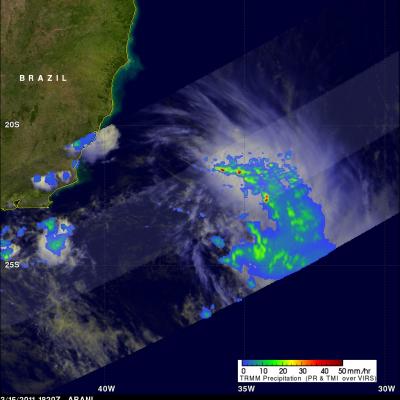
The TRMM satellite had another very good view of subtropical cyclone ARANI in the morning light on 16 March 2011 at 1052 UTC. This orbit showed that there were very heavy thunderstorms in the eastern half of the storm. TRMM's Precipitation Radar (PR) showed that some of these powerful storms were reaching to heights of over 14 km (~8.7 miles) above the surface of the south Atlantic Ocean.