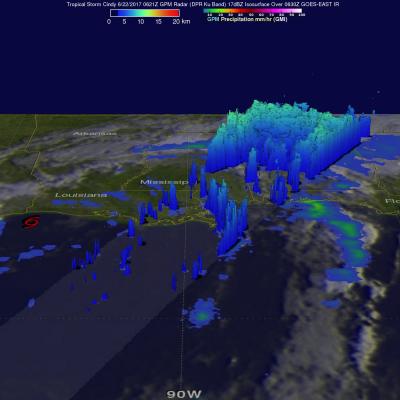
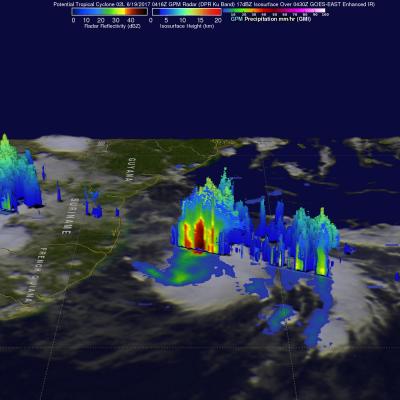
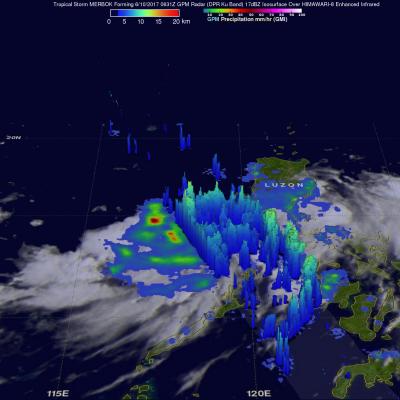
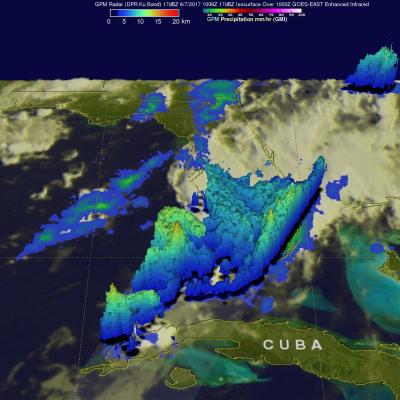
V04A IMERG Early GIS friendly products now available
PPS has completed the production of the GIS-friendly TIF/TFW products created from the IMERG Early dataset. These products include running accumulations at 3hr and 1day. The Early TIF/TFW GIS-friendly products have been created back to the beginning of the mission: March 2014. They can be found on jsimpson server in the directories: /NRTPUB/imerg/gis/early/YYYY/MM Documentation for the TIF/TFW products is contained in the document README.GIS.pdf in /NRTPUB/imerg/gis.