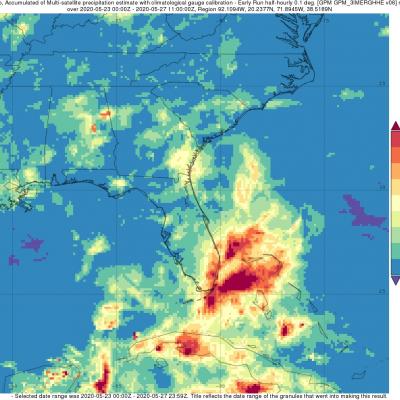
Short-lived Bertha Brings Heavy Rains to Parts of Florida
Bertha was a named storm for just the briefest of periods, becoming a tropical storm on the morning of Wednesday May 27th at 8:30 am EDT just one hour before it made landfall along the South Carolina coast near Charleston. After making landfall, Bertha quickly weakened into a tropical depression and was then accelerated northward by the southerly flow between a deep trough of low pressure over the Mississippi Valley to the west and a ridge of high pressure located just off the US East Coast. Because of this, rainfall totals over the Carolina’s were not very heavy. Bertha’s biggest impact actually occurred when it was still in the formation process, before it became organized enough to be named. On Monday May 25th, a trough of low pressure became established over the Florida Straits, initiating shower and thunderstorm activity in the region. Over the next day, as this trough, which extended eastward over the warm waters of the Gulf Stream and eventually led to Bertha, slowly moved northward up the Florida peninsula, it provided a focus for showers and thunderstorms, which brought heavy rains to southeast Florida.