Rainfall Floods the Mississippi River
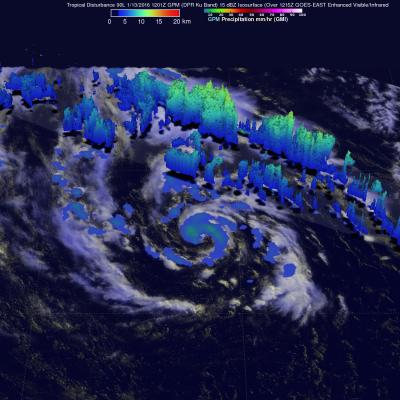
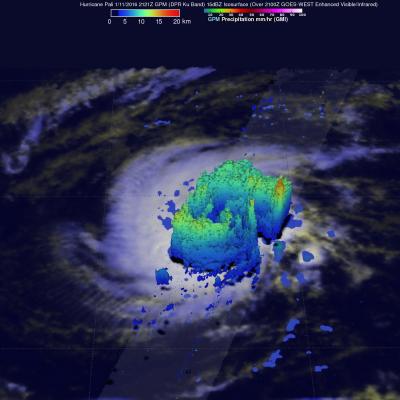
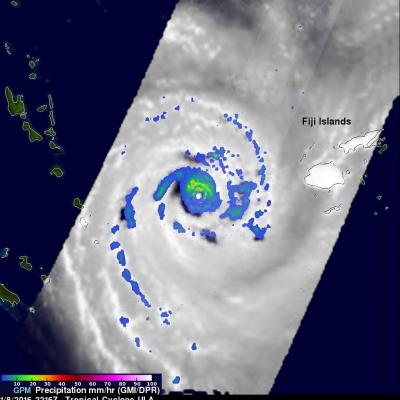
A series of winter storms brought more than 20 inches of rainfall to the Midwest and southeastern United States in December 2015. Massive flooding followed throughout both the regions. An animation of rainfall data from those storms was created at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland.