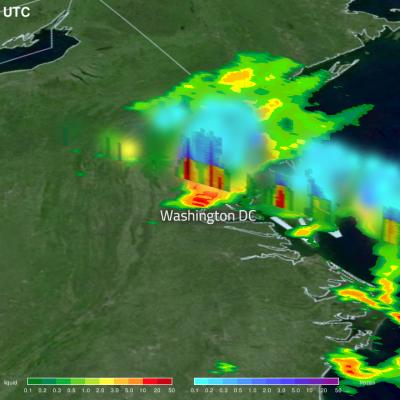
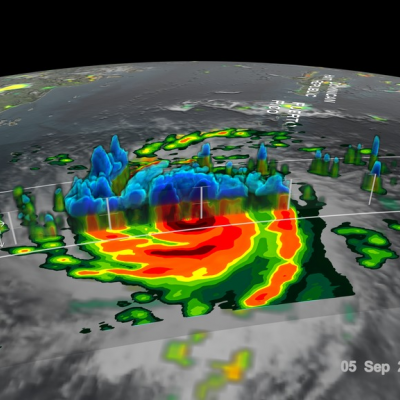
GPM Flies Over Flooding Rainfall in Washington DC
Washington DC experienced extreme rainfall the morning of July 8th, 2019 when a cluster of slow-moving thunderstorms moving through the area tapped into a very moist airmass to produce extremely heavy rains, which resulted in flash flooding throughout the region. The storms were triggered by a nearby frontal boundary. The GPM Core Observatory passed over this storm system at 8:51am ET, with its Dual-frequency Precipitation Radar measuring rainfall rates in excess of 100 mm/hr in some areas. Reagan National Airport (DCA) also reported receiving 80 mm of rainfall in one hour, corroborating the