GPM Examines Forming Tropical Storm Nate (TD16)
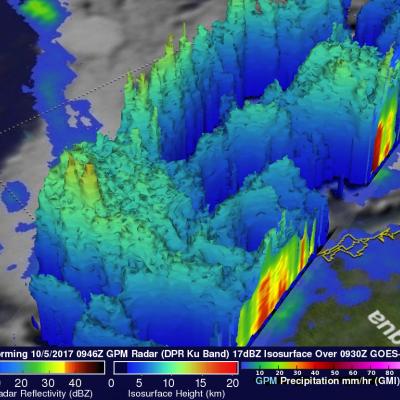
The GPM core observatory satellite passed above forming tropical storm Nate (TD16) on October 5, 2017 at 5:46 AM EDT (0946 UTC). TD16 was located in the western Caribbean near the coast of Nicaragua with winds of about 34.5 mph (30 kts). Data received by GPM's Microwave Imager (GMI) and Dual-Frequency Precipitation Radar (DPR) shows bands of rain producing heavy rainfall East of TD16's center of circulation. Downpours in the Caribbean Sea East of Nicaragua were measured by GPM's Radar (DPR Ku Band) dropping rain at a rate of over 6.4 inches (162 mm) per hour. This close-up 3-d cross section