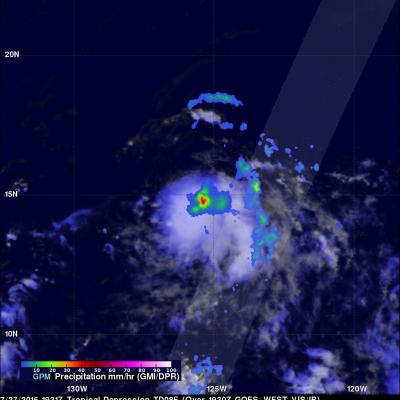
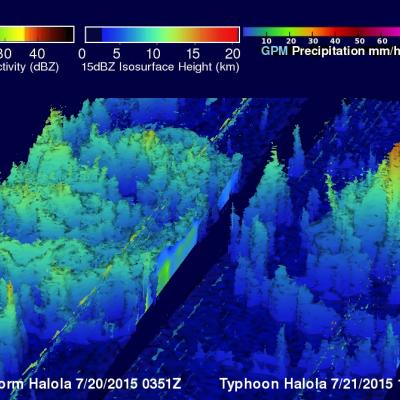
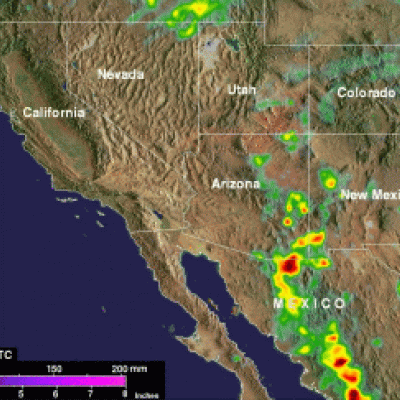
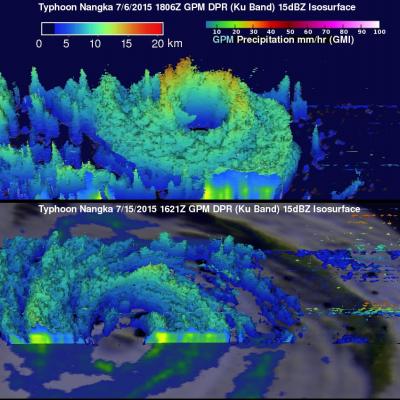
TD08E Formation Monitored By GPM
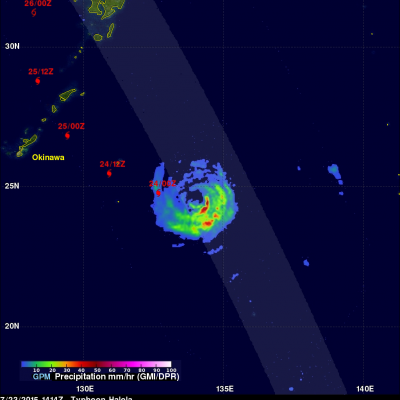
The GPM core observatory satellite flew over forming tropical depression 08E on July 27, 2015 at 1931 UTC ( 12:31 PM PDT). Rainfall was measured by GPM's Microwave Imager (GMI) and Dual-Frequency Precipitation Radar (DPR) falling at a rate of 50 mm (almost 2 inches) per hour in storms near the center of the tropical depression. The National Hurricane Center (NHC) predicts that TD08E will not intensify very much because northwesterly vertical wind shear is retarding development. GPM's DPR instrument scan (shown in lighter shades) viewed an area east of the center of the developing tropical