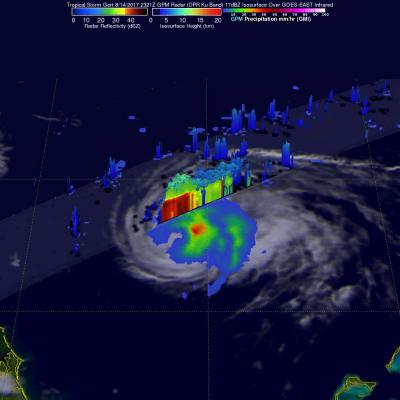
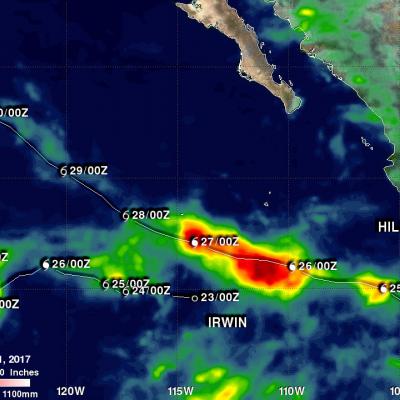
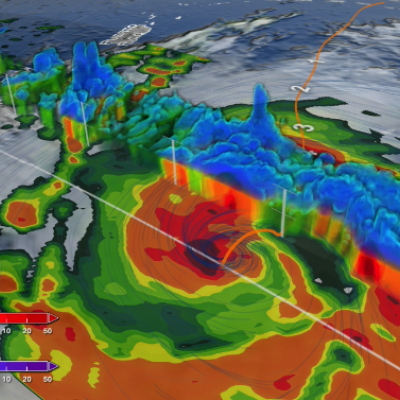
NASA's IMERG Shows Rainfall Accumulation Along Harvey's Track
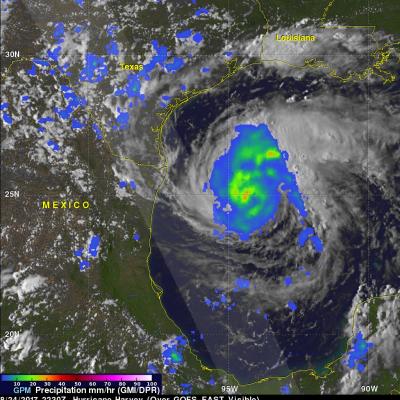
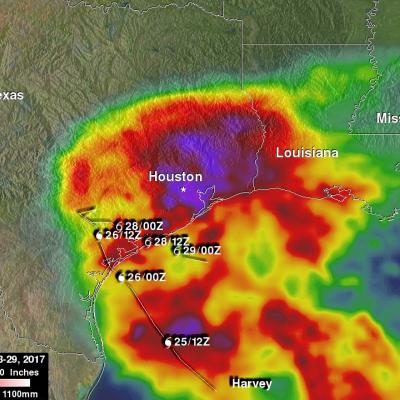
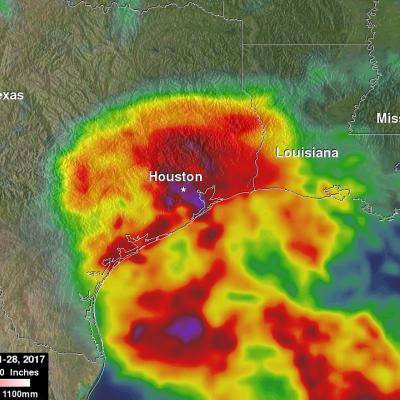
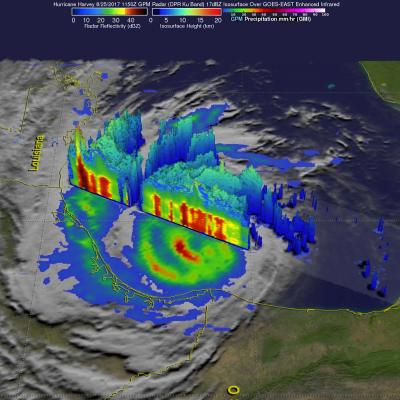
Total rainfall estimates from NASA's Integrated Multi-satelliE Retrievals for GPM (IMERG) data are shown here for the period from August 23-29, 2017. During this period hurricane Harvey dropped heavy rainfall as it moved through the Gulf Of Mexico and stalled over Texas. It has been reported that Harvey dropped over 40 inches (1016 mm) of rain over southeastern Texas during this period. Hurricane Harvey's locations and track are shown here overlaid in white IMERG Data are produced using data from the satellites in the GPM Constellation, and is calibrated with measurements from the GPM Core