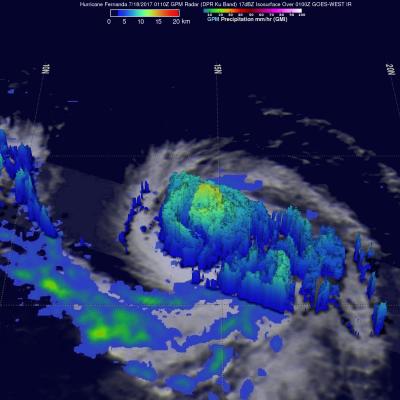
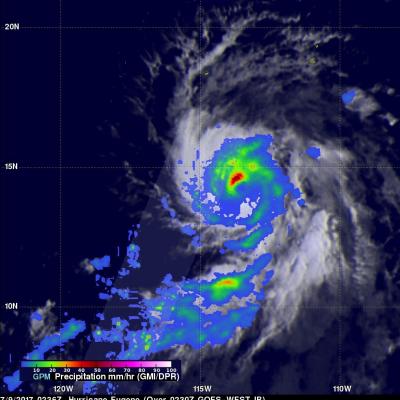
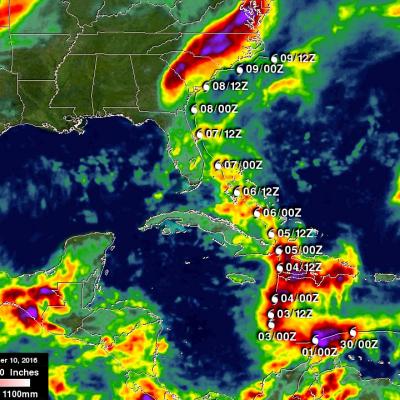
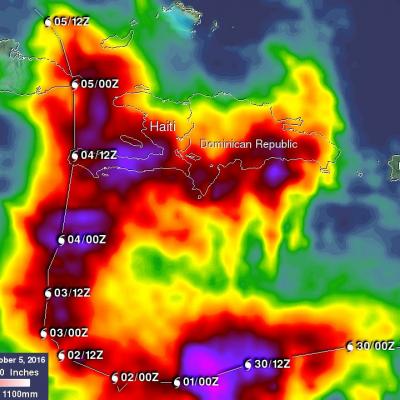
GPM Views Dissipating Hurricane Fernanda
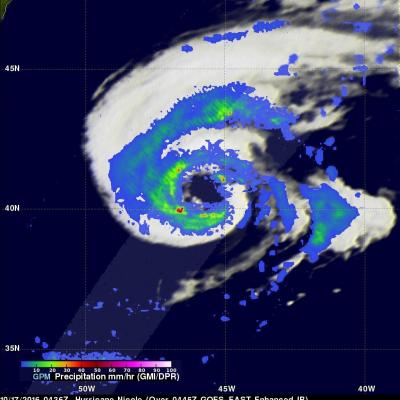
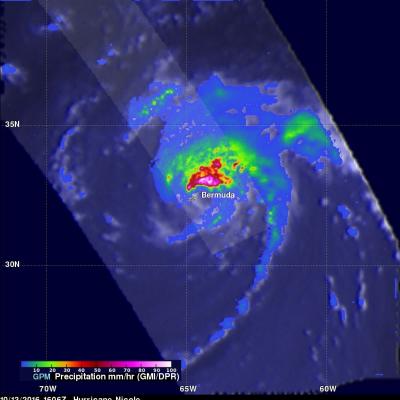
The GPM core observatory satellite had another exceptional view of hurricane Fernanda when it flew over on July 20, 2017 at 0101 UTC. GPM saw a much different hurricane than it viewed a couple days earlier. GPM's Microwave Imager (GMI) and Dual-Frequency Precipitation Radar (DPR) radar instruments found that the dissipating hurricane only contained heavy rainfall in it's northwestern quadrant. Cooler water, dry air, and southwesterly vertical wind shear had caused Fernanda to weaken. GPM's Radar revealed that powerful convective storms in that part of the dissipating hurricane were still