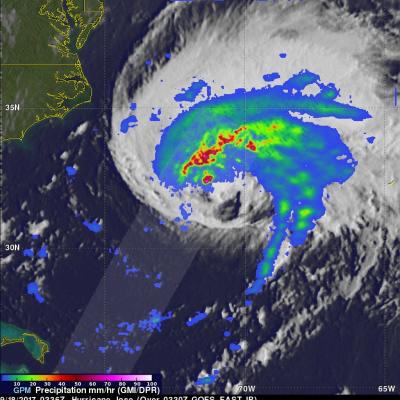
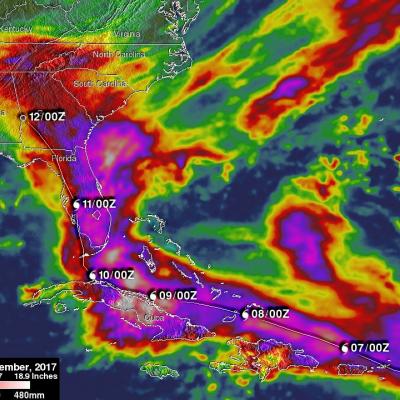
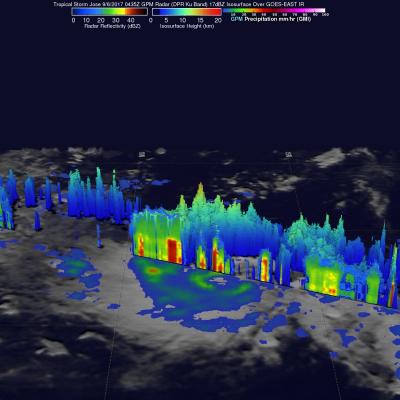
Jose Continues to Meander off the East Coast
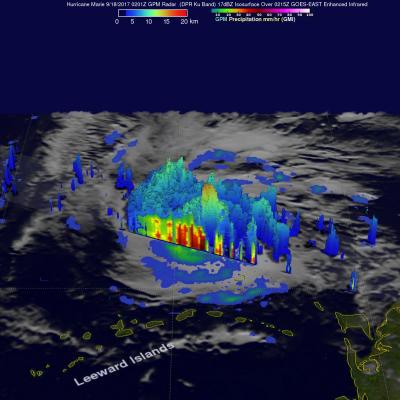
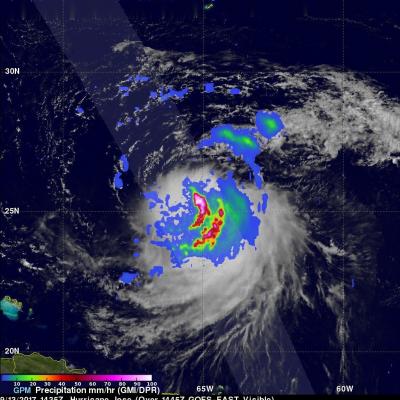
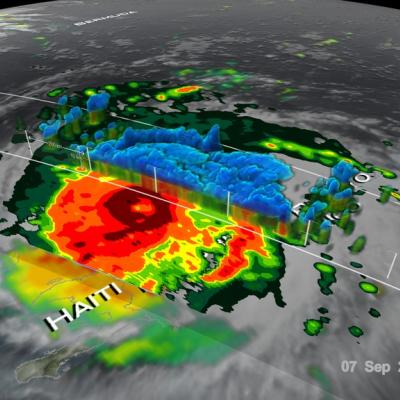
Jose has been a named storm for nearly two weeks now as it continues to slowly move northward off the US East Coast east of the Outer Banks of North Carolina. At one time, Jose was a powerful category 4 border line category 5 storm with maximum sustained winds reported at 155 mph by the National Hurricane Center back on the 9th of September as it was approaching the northern Leeward Islands. Jose passed northeast of the Leeward Islands as a category 4 storm on a northwest track and then began to weaken due to the effects of northerly wind shear. Jose then made a counterclockwise loop about