GPM Core Observatory Centrifuge Testing

NASA technicians spun the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) satellite up to just over 10 RPM in Goddard Space Flight Center’s High-Capacity Centrifuge facility March 31. At that speed, the spin exerted a lateral pressure of 2.4 G’s, or 2.4 times the force of gravity on the satellite.
Spin tests such as these are used to determine whether the forces of launch could adversely affect hardware we put into space, and to test spacecraft chassis design.
DROP Ground Validation Instruments
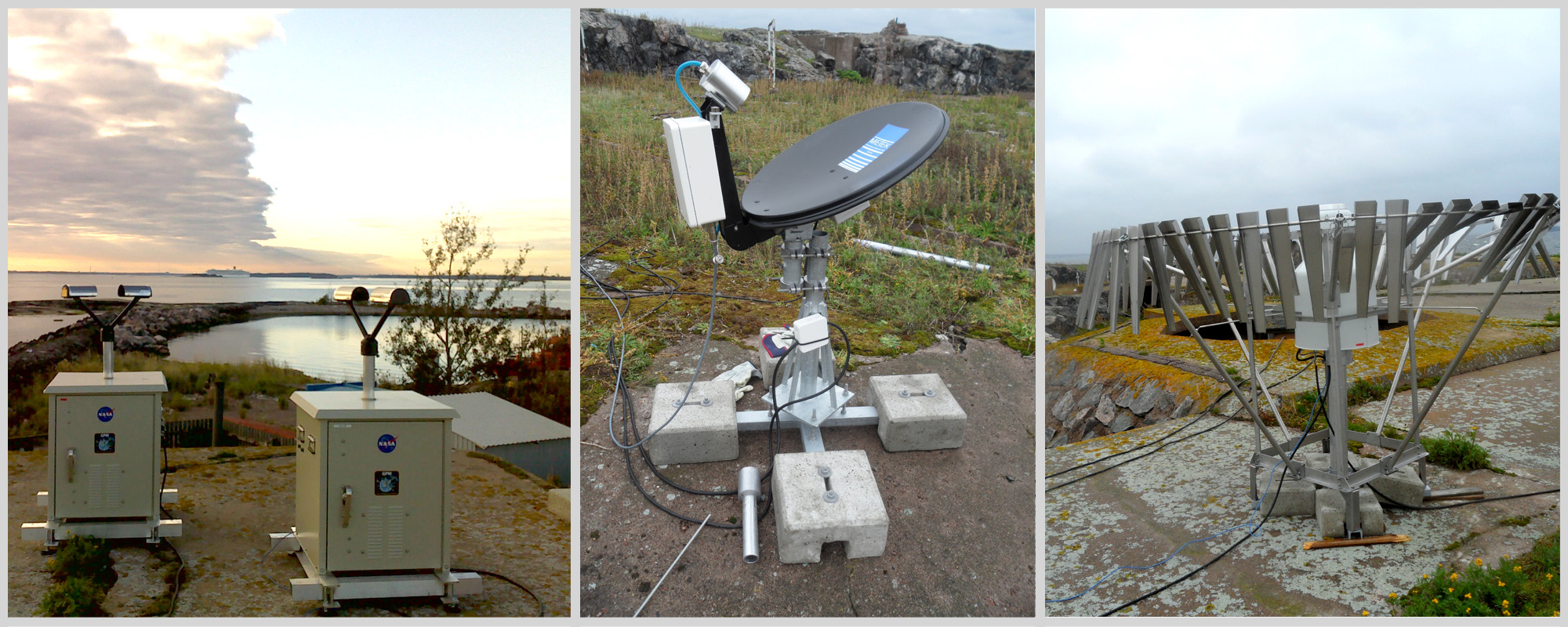

Various ground validation instruments, including the Parsivel Disdrometer in Finland, a Micro Rain Radar, and a Pluvio Snow guage
NPOL Ground Validation Instrument
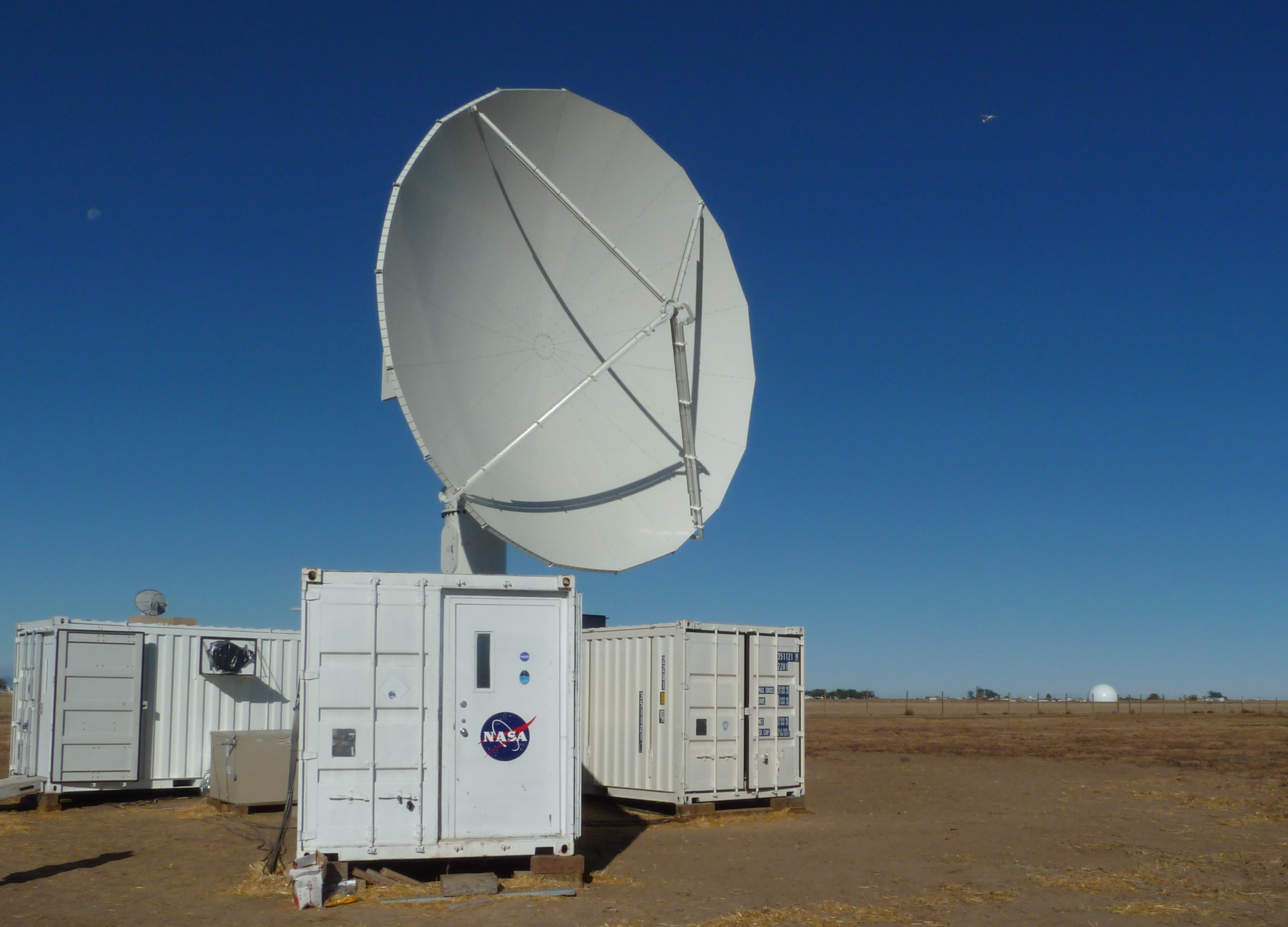

The NPOL underwent a complete antenna system upgrade in 2010 and is one of two fully transportable research-grade S-band systems in the world. It is used to make accurate volumetric measurements of precipitation including rainfall rate, particle size distributions, water contents and precipitation type.
GPM Ground and Airborne Validation Diagram
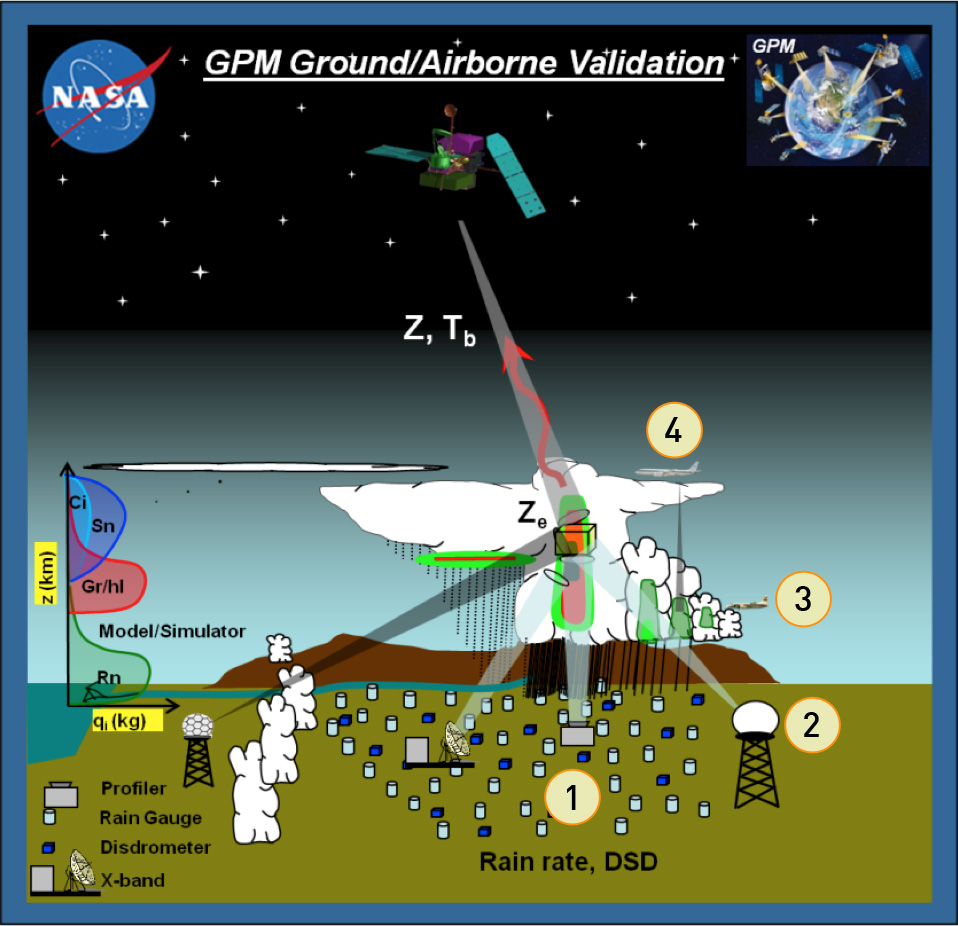
- Ground level suites of high density