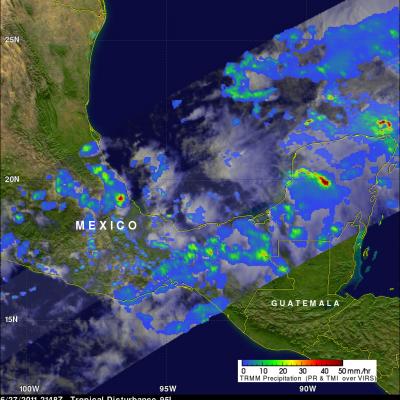
The TRMM satellite flew over an area of disturbed weather labeled 95L affecting southern Mexico on 27 June 2011 at 2148 UTC (5:48 PM EDT). The TRMM rainfall analysis shown above used TRMM's Microwave Imager (TMI) and Precipitation Radar (PR) data. It shows that heavy rainfall of over 50mm (~2 inches) associated with 95L was occurring in southern Mexico northwest of Veracruz and over the Yucatan Peninsula. Some of this very heavy rainfall may result in flash flooding and mudslides. The National Hurricane Center (NHC) is watching this area and has indicated that there is a slight chance that a
Successful Completion of KDP-C Review
GPM has successfully completed the GPM Mission Key Decision Point - C (KDP-C) Review on December 2, 2009, which formally confirms the Implementation phase of the GPM Mission. Key Decision Point C (KDP-C) is the agency-level approval for the project to begin implementation, and baselines the project’s official schedule and budget. The review process for KDP-C starts with the Preliminary Design Review/Non-Advocate Review (PDR/NAR) to the project’s Standing Review Board (SRB). Next, the project and SRB report to the GSFC Center Management Council at the Confirmation Readiness Review (CRR). Based