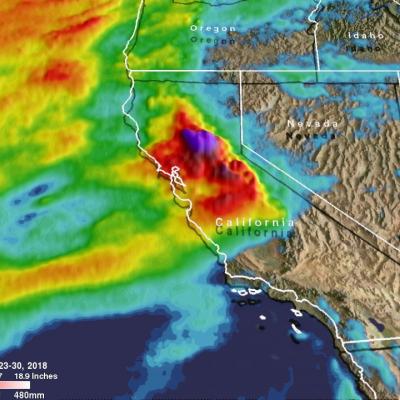
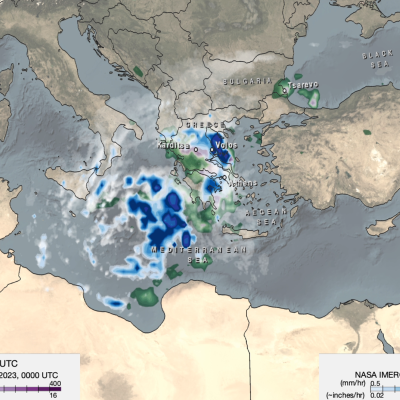
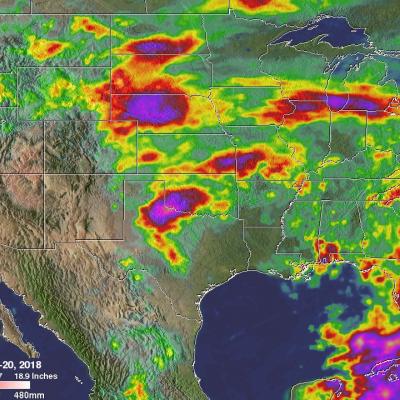
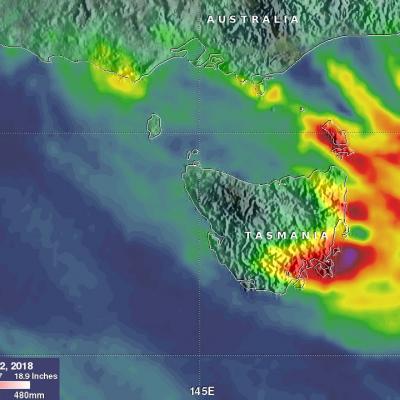
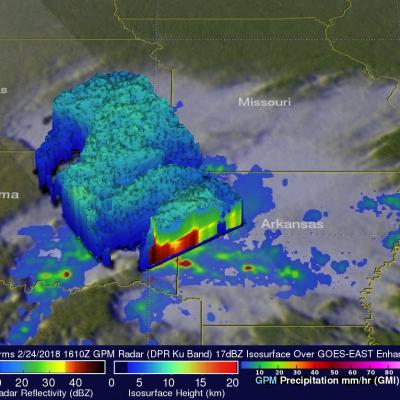
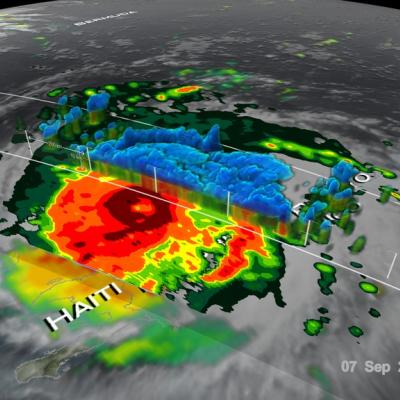
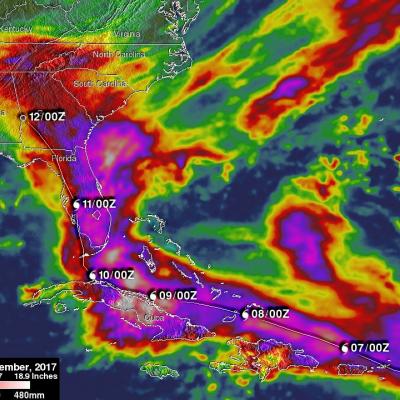
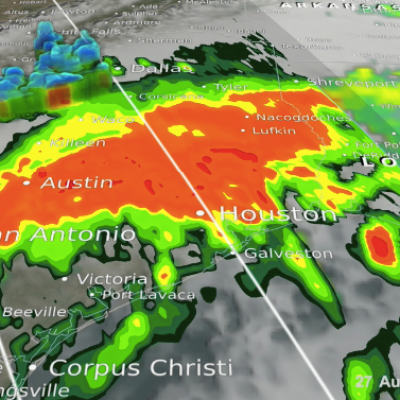
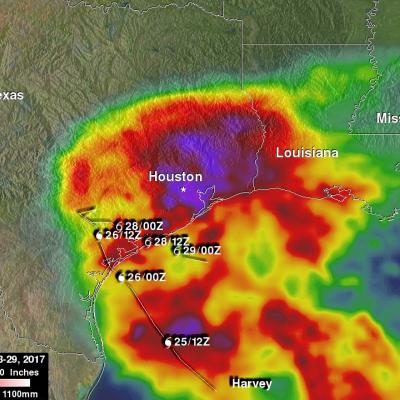
IMERG Measures Flooding Rainfall In Deadly California Wildfire Areas
Heavy precipitation has been falling in areas of California that were recently devastated by deadly wildfires. This flooding rainfall has resulted in evacuations in burn scarred areas such as Butte County where the deadly Camp Fire hit this month. Flash floods, debris flows and mudslides are now predicted in areas where deadly wildfires stripped away vegetation. On a positive note these Pacific storms are expected to dampen wildfires and replenish the Sierra Nevada snowpack. This snowpack is an important source of water for California's streams and rivers. NASA's Integrated Multi-satellitE