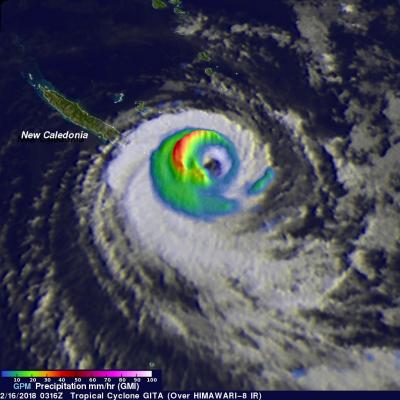
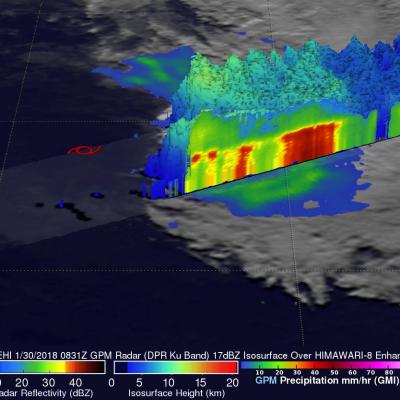
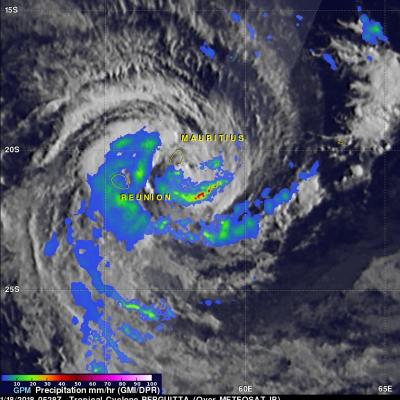
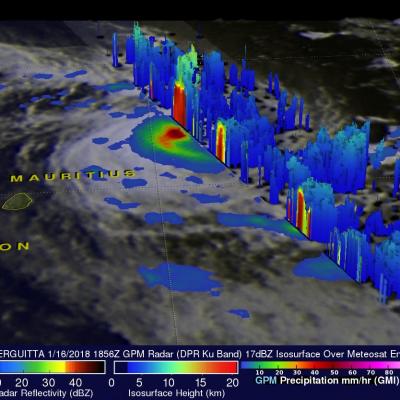
Cyclones Gita's Rainfall Measured With GPM's Microwave Imager (GMI)
The GPM core observatory satellite's Microwave Imager (GMI) instrument had a fairly good view of tropical cyclone GITA on February 2018 at 0316 UTC. GPM's Dual Frequency Precipitation Radar (DPR) swath only scanned the area west of GITA's main area of precipitation. The weakening tropical cyclone was passing the southeastern tip of New Caledonia. Although weakening, GITA still had winds estimated at over 90 kts (104 mph). Rainfall derived from GMI data showed that the heaviest precipitation, falling at rate of about 51 mm (2 inches) per hour, was shown west of GITA's low level circulation