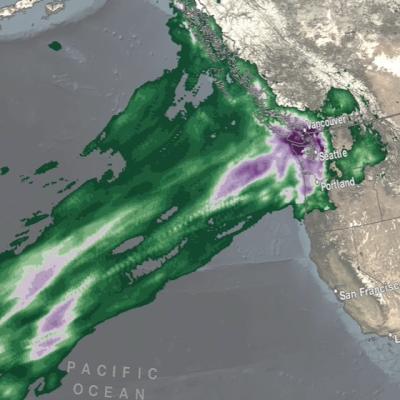
Tropical Cyclone Freddy first made landfall along the east coast of Madagascar just north of the town of Mananjary on Feb. 21, 2023, as a Category 3 cyclone with average winds reported at ~81 mph (130 km/h) and gusts up to ~112 mph (180 km/h). After crossing over Madagascar Freddy continued westward over the Mozambique Channel before making landfall again along the east coast of Mozambique just south of Vilankulos as a moderate tropical storm with sustained winds estimated at 50 mph. Despite being weaker at landfall, Freddy caused widespread flooding across parts of Mozambique due to the storm stalling out near the coast after making landfall. Incredibly, Freddy drifted back out over the Mozambique Channel, nearly making landfall along the southwest coast of Madagascar. It then changed direction, re-intensified, weakened, re-intensified one last time, and made landfall once again on March 11 near Quelimane, Mozambique, as a Category 1 cyclone with sustained winds reported at 90 mph.