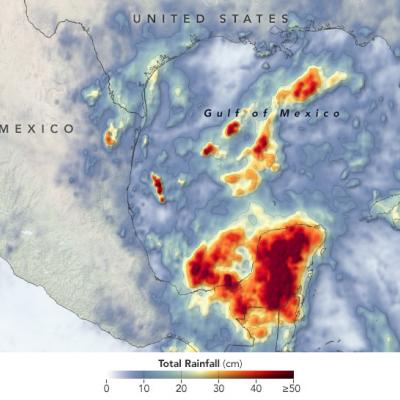
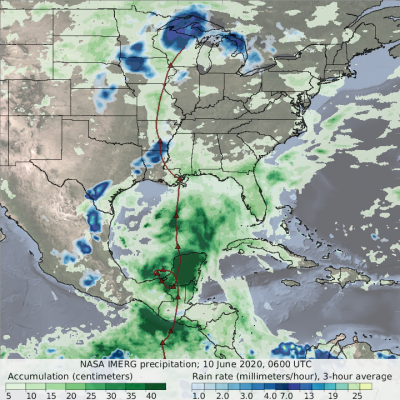
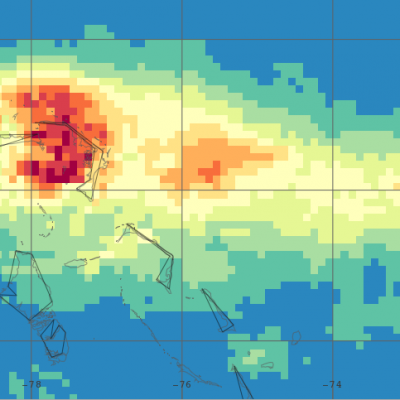
Cristobal Drenches Central America
The 2020 Atlantic hurricane season is off to a busy start. By the first week of June, Tropical Storm Arthur had already brushed North Carolina, Tropical Storm Bertha had drenched South Carolina, and the third named storm of the year— Cristobal—was dropping torrential rain on the Yucatán Peninsula. The storm first developed in the Pacific in late May as Tropical Storm Amanda, spinning off the southern end of a seasonal low-pressure pattern called the Central American Gyre. After making landfall in Guatemala and causing deadly floods in El Salvador, Amanda weakened and became less organized as