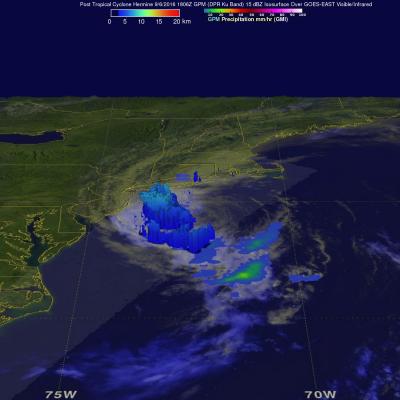
GPM Takes Parting Look At Hermine
Post Tropical Cyclone Hermine was still rotating in the Atlantic Ocean east of New Jersey when the the GPM core observatory satellite flew above on September 6, 2016 at 2:05 PM EDT ( 1806 UTC). Hermine's power was greatly dissipated from the hurricane that hit Florida on September 2, 2016. Hermine still had maximum sustained winds of about 58 mph (50 kts). Hermine was also still producing some light to moderate showers. Precipitation data shown here were derived from GPM's Microwave Imager (GMI) and Dual-Frequency Precipitation Radar (DPR) instruments. Those data showed that rain was falling