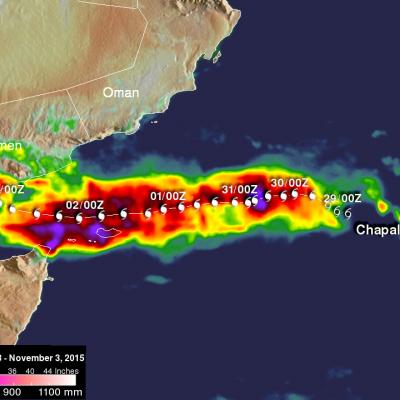
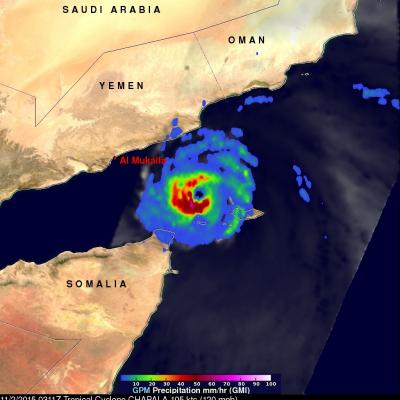
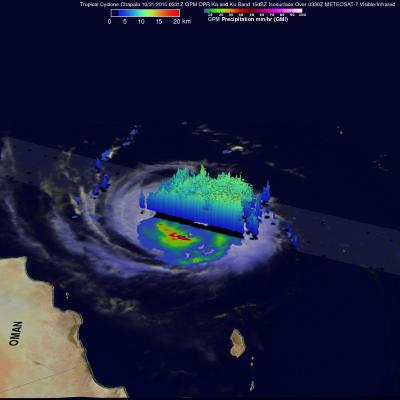
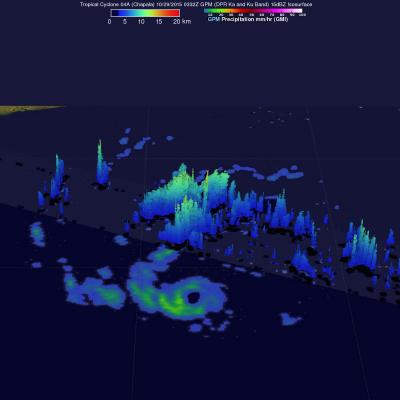
Cyclone Chapala Brings Heavy Rains, Flooding to Yemen
Cyclone Chapala, which formed into a rare but powerful Category 4 cyclone in the Arabian Sea with winds at one time estimated at 155 mph by the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) back on the 30th of October, made its initial landfall along the south coast of Yemen this morning west of the port city of Mukulla at around 09:00 UTC as a Category 1 cyclone with maximum sustained winds estimated at 75 mph by JTWC, making it the first Category 1 cyclone on record to strike Yemen. The last cyclone to strike the Arabian peninsula was Cyclone Phet, which hit eastern Oman back in 2010. In addition to