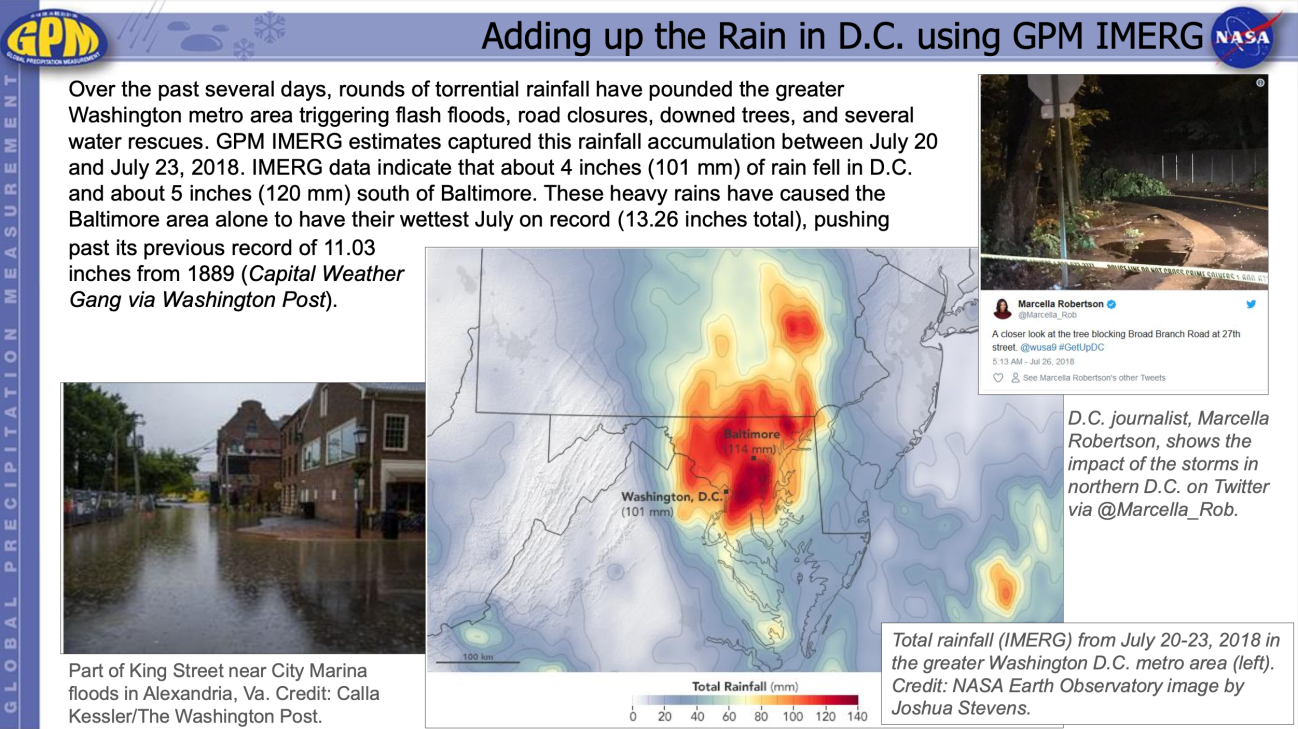
Water and Agriculture
Growing human population, increased demand for water and energy, and a changing climate have contributed to expanded concerns centered on freshwater resources and food supply and production. Both water resource managers and the agricultural community need to know the amount and distribution of seasonal rainfall and the timing of the onset of rainfall to prepare for freshwater shortages and forecast crop yields. Remotely sensed precipitation estimates play a key role in predicting changes in freshwater supply and agricultural forecasting. The Water Resources, Agricultural Forecasting, and Food Security Applications area promotes the use of precipitation data from the GPM constellation to analyze and forecast changes that affect water resources and its subsequent impact on agricultural productivity.