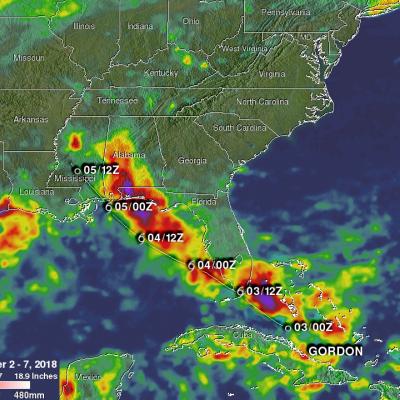
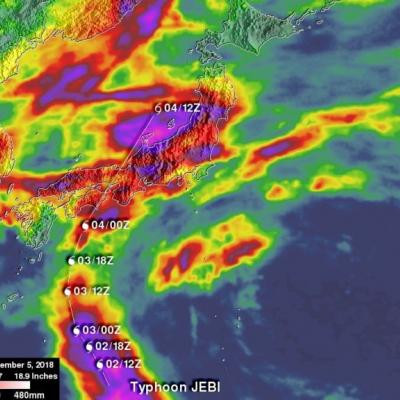
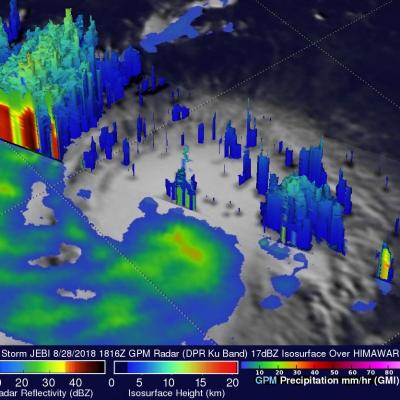
GPM Observes Dangerous Super Typhoon Heading Toward The Philippines
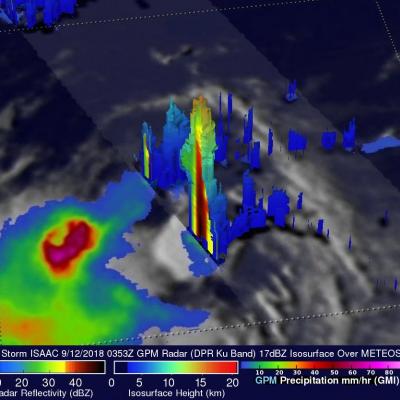
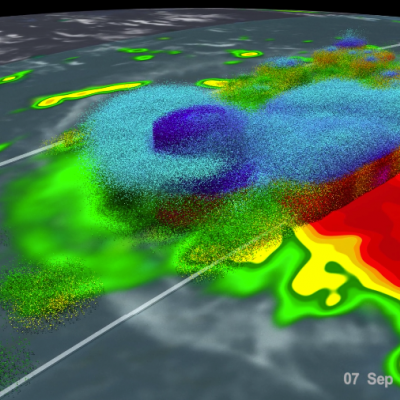
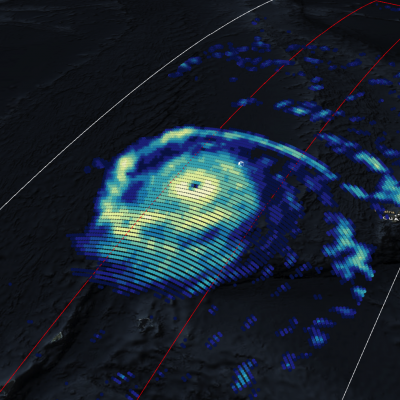
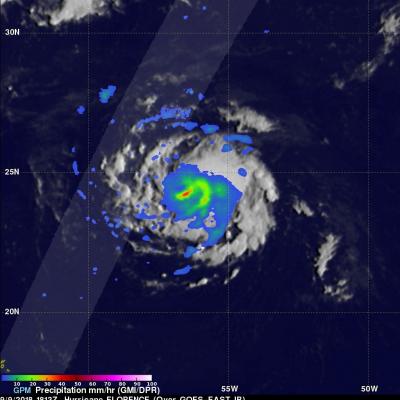
The GPM core observatory satellite has recently provided very useful information about super typhoon MANGKHUT in the western Pacific Ocean. A few days ago MANGHUT battered the Marianas Islands. MANGKHUT's destructive winds pounded the island of GUAM causing power outages and it's extremely heavy rainfall caused flash floods. The GPM core observatory satellite passed over super typhoon MANGKHUT on September 11, 2018 at 0407 UTC when it was west of GUAM. GPM's Microwave Imager (GMI) and Dual-Frequency Precipitation Radar (DPR) collected data showing that MANGKHUT was a large and very well