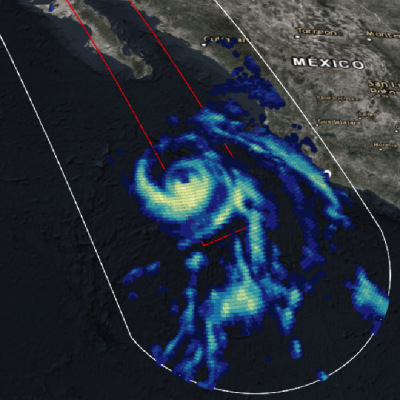
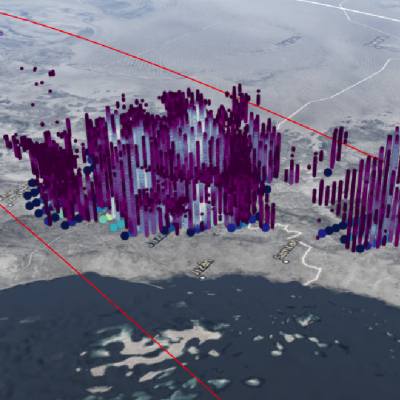
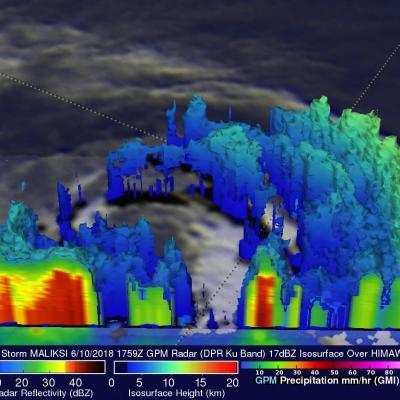
GPM Flies Over Hurricane Bud off the Coast of Mexico
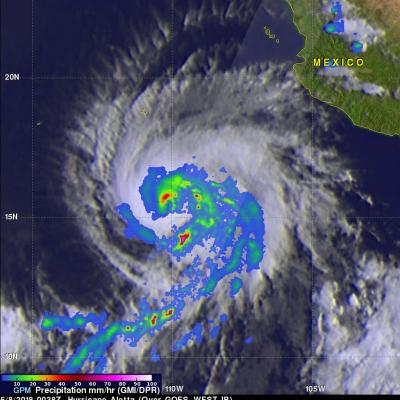
View full-screen in STORM Event Viewer The GPM core observatory satellite passed above hurricane BUD in the eastern Pacific Ocean on June 12, 2018 at 5:27 PM MDT (2327 UTC). BUD's movement over colder waters had caused it's eye to become less defined. Data collected by GPM's Microwave Imager (GMI) showed that moderate to heavy precipitation was only present in the southeastern quadrant of the weakening hurricane. GPM's GMI also indicated that the heaviest rainfall in the area, of over 78 mm (3.1 inches) per hour, was occurring near Mexico's coastline well to the northeast of BUD's center of