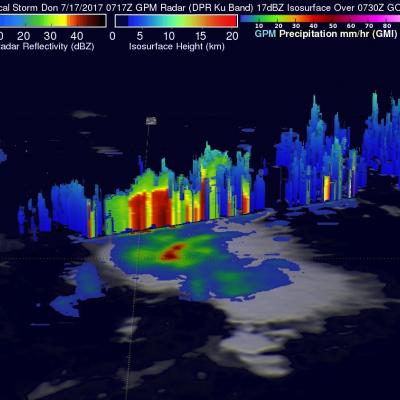
Forming Tropical Storm Don's Rain Checked By GPM
On Monday July 17, 2017 at 5:00 PM EDT a tropical disturbance in the Atlantic Ocean was upgraded to tropical storm Don, the fourth Atlantic Tropical storm of 2017. The GPM core observatory satellite flew above the forming tropical storm much earlier in the same day at 3:17 AM EDT (0717 UTC). GPM's Microwave Imager (GMI) and Dual-Frequency Precipitation Radar (DPR) instruments collected data that were used to evaluate precipitation within the forming tropical cyclone. GPM's Radar data swath (shown in lighter shades) covered an area to the west of the greatest amount of rainfall. GPM's radar