GPM Sees Intensifying Tropical Storm Franklin
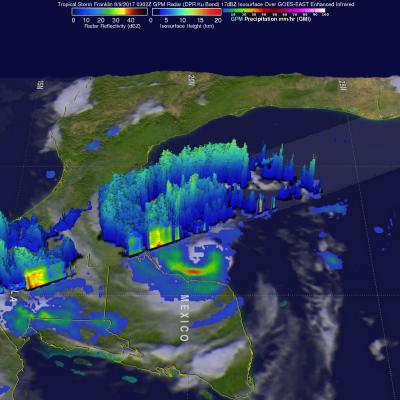
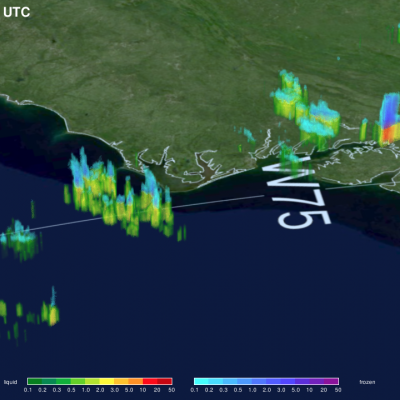
The GPM core observatory satellite had an informative pass over Tropical storm Franklin on August 9, 2017 at 0302 UTC. The intensifying tropical storm had moved from Mexico's Yucatan Peninsula into the southwestern Gulf Of Mexico's Bay of Campeche. GPM's Microwave Imager (GMI) and Dual-Frequency Precipitation Radar (DPR) data showed that Franklin contained a few heavy bands of convective rainfall. GPM's DPR found rain falling at a rate of over rain 2.4 inches (62 mm) per hour in bands of intense storms moving around the southwestern side of the storm. This 3-D view of tropical storm Franklin