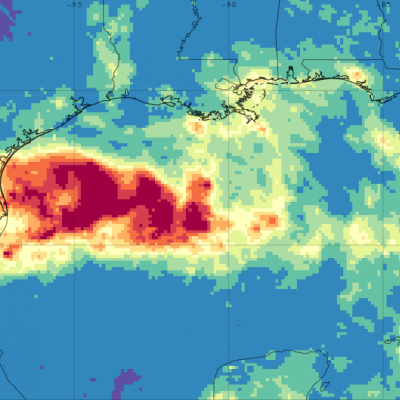
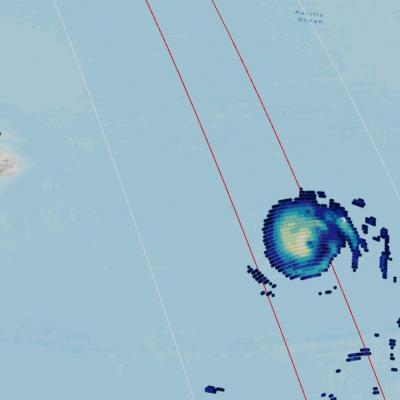
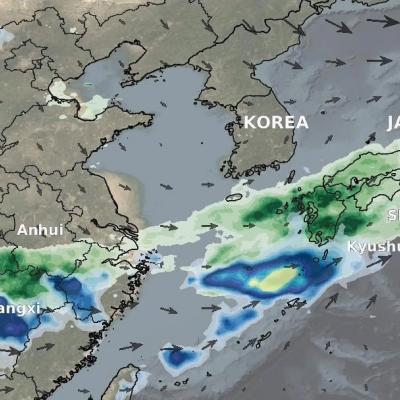
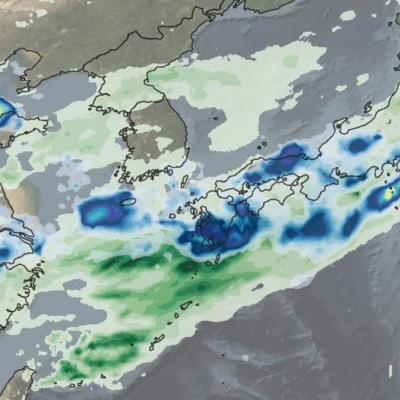
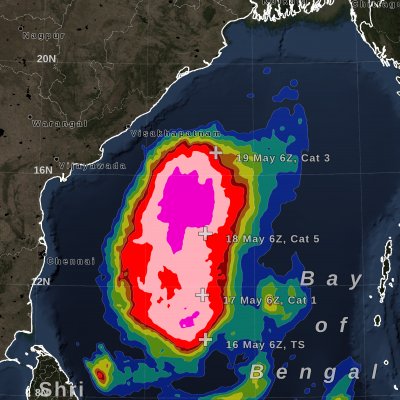
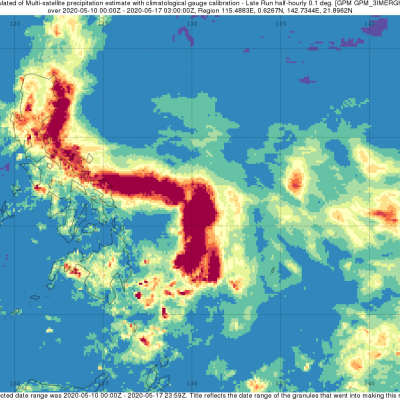
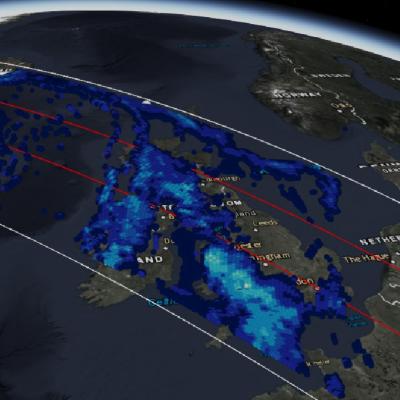
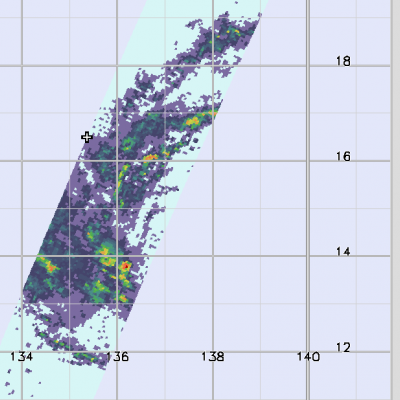
Weather
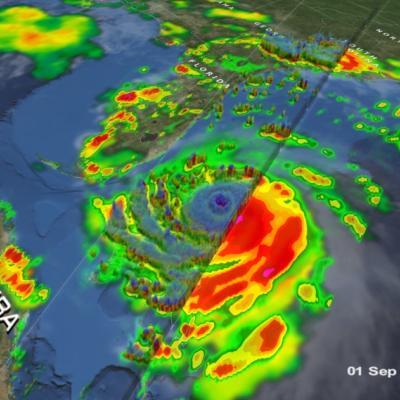
Earth’s climate is changing. The accumulation of greenhouse gases has affected the oceans and ice systems as well as the atmosphere, which in turn impacts the water cycle. To predict future changes in weather and climate and estimate environmental variables, scientists use sophisticated computer models. These models rely on available global data to describe the conditions that exist today to project how conditions may change in the future. GPM’s Weather, Climate, and Land Surface Modeling Applications area promotes the use of precipitation measurements from GPM satellites to help model future behavior of precipitation patterns and climate.