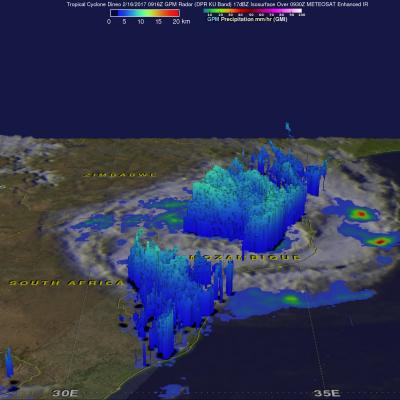
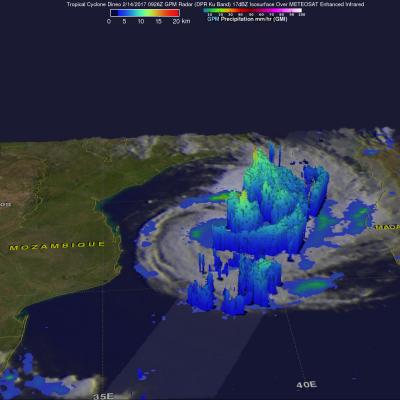
GPM Examines Deadly Tropical Cyclone Dineo
Dineo has now weakened to a tropical depression but the tropical cyclone had winds of over 70 kts (80.5 mph) when it hit Mozambique. Four people have been reported killed by Dineo. The GPM core observatory satellite flew over Mozambique on February 16, 2016 at 0916 UTC after Dineo's maximum sustained winds had fallen to about 60 kts (69 mph). Data collected by GPM's Microwave Imager (GMI) and Dual-Frequency Precipitation Radar (DPR) instruments showed that the tropical cyclone was still dropping light to moderate rainfall over a large area of southern Mozambique. This GPM view revealed that