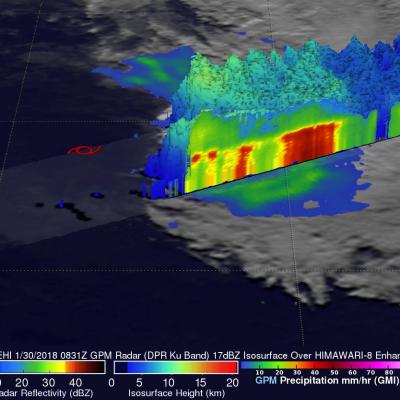
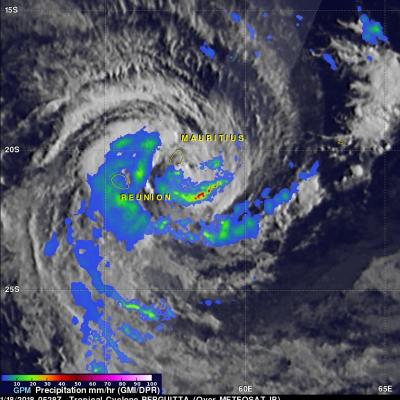
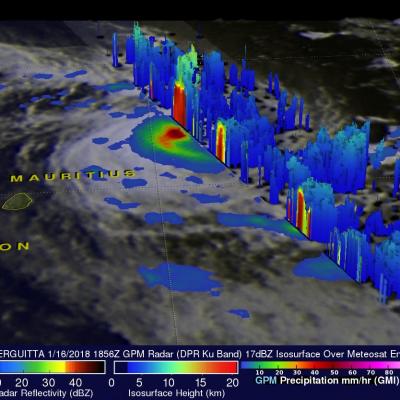
Weakening Tropical Cyclone Cebile Examined By GPM
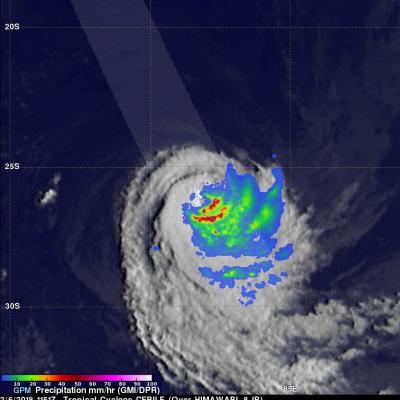
The GPM core observatory satellite passed above weakening tropical cyclone CEBILE on February 6, 2018 at 1151 UTC. CEBILE's maximum sustained winds had decreased to about 40 kts (46 mph). The satellite showed that most of the convective rainfall in the sheared tropical cyclone was southeast of CEBILE's center of circulation. Dual Frequency Precipitation Radar (DPR) data received by GPM with this pass showed that the northeastern side of the eye wall was eroding while continuous heavy precipitation was found by GPM in the southeastern quadrant of the storm. The area scanned by GPM's DPR is