Applications
Overview
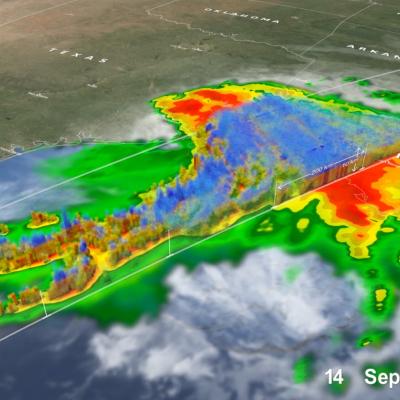
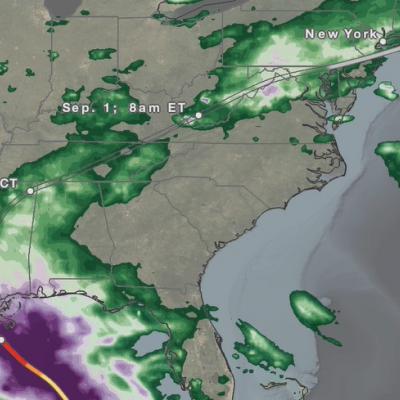
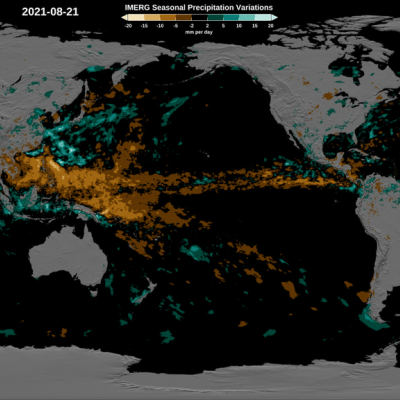
The Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) mission has several cross-cutting application areas which contribute to and enhance our understanding of weather forecasting, disasters, ecology, health, water and agriculture and energy. Using advanced space-borne instruments, GPM measures light rain to heavy rain and falling snow, producing a near-global view of precipitation every 30 minutes. Through improved measurements of rain and snow, precipitation data from the GPM mission is used by a diverse range of applications and user communities at local to global scales to inform decision making and policy that directly benefits society.
What are Applications?
“Applications” refers to the use of mission data products in decision-making activities for societal benefit. Mission Applications take a satellite's data products and expands them into areas where they can help inform policy or decisions.
Learn more about Applied Sciences at NASA
Who's Using GPM Data?
Learn about the different people and organizations that are using GPM and other NASA Earth data to help improve life around the world.
GPM Mentorship Program
NASA’s GPM applications team and University of Coimbra’s Earth and Space Science Center (CITEUC Portugal) have collaborated to host the GPM Mentorship Program for several years.
The program supports new and existing user communities to provide a tailored hands-on learning experience in using GPM data for applications. It provides participants with training and tools to use state-of-the-art GPM satellite-based precipitation estimates, and helps them apply GPM data to support real-world problems and benefit their communities.
Learn more about each GPM Mentorship Program session: 2024, 2023, 2022
GPM Data for Decision Making
Are you using GPM satellite precipitation data in your work, or would you like to? Share your story with our team, or ask us any questions you may have using our contact form.
We also encourage you to get involved in GPM applications by attending an applications event or accessing the free and publicly available data in the data section of this site.
- Dalia Kirschbaum (NASA GSFC), GPM Mission Associate Deputy Project Scientist for Applications
- Andrea Portier (NASA GSFC / SSAI), GPM Applications and Outreach Coordinator
- Dorian Janney (NASA GSFC / ADNET), GPM Outreach Specialist
- Jacob Reed (NASA GSFC / Telophase), GPM Web Developer
- GPM Applications Posters (.zip / .pdf)
- GPM Applications & Data Access One Pagers (.pdf)
- Highlights
Applications Featured Resources
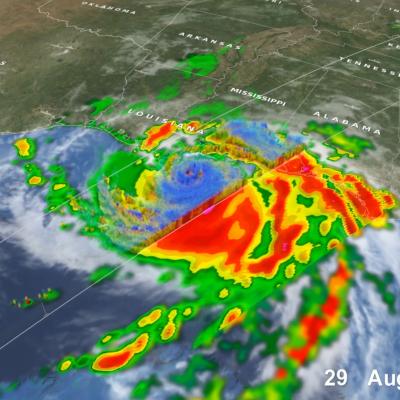
GPM IMERG precipitation rates and totals from Tropical Cyclone Freddy, Feb. 6 - March 12, 2023. Credit: NASA
Download in high resolution from the NASA Goddard Scientific Visualization Studio
In a series of three half-day virtual meetings, this workshop will focus on current applications and future opportunities of NASA precipitation and cloud data products to support transport and logistical activities for aviation, maritime, roads and highway transportation systems. The workshop will bring together representatives from federal and state operational agencies and private companies to discuss how NASA precipitation and cloud products could be better leveraged to inform decision-making for transport and logistical operations. The workshop will also provide an opportunity for end...
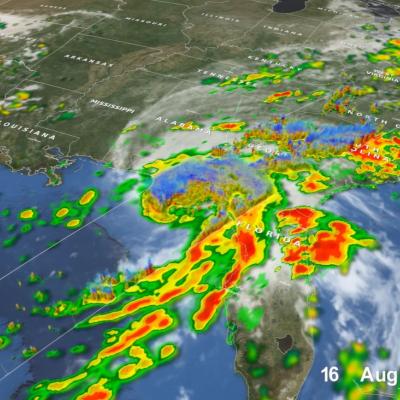
Cameras outside the International Space Station captured dramatic views of Hurricane Zeta at 12:50 pm ET October 28, as it churned 200 miles south-southwest of New Orleans packing winds of 90 miles an hour. Credit: NASA International Space Station
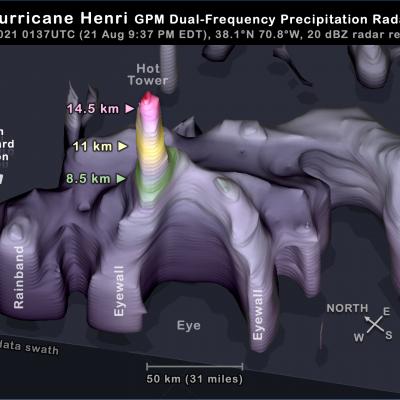
GPM Core Observatory overpass of Tropical Storm Zeta on October 28 at approximately 3:25am CDT (8:25 UTC). Credit: NASA Goddard Scientific Visualization Studio
View an interactive 3D visualization of this overpass in STORM Event Viewer