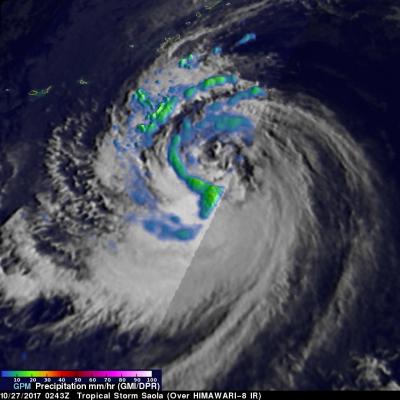
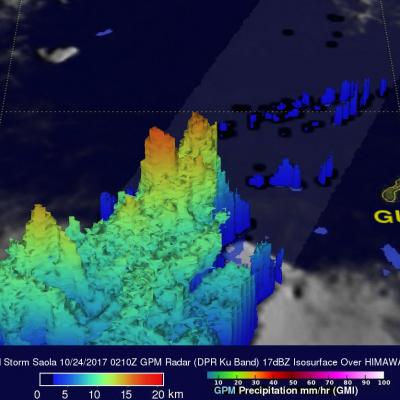
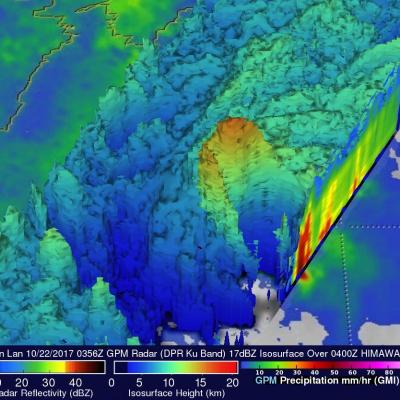
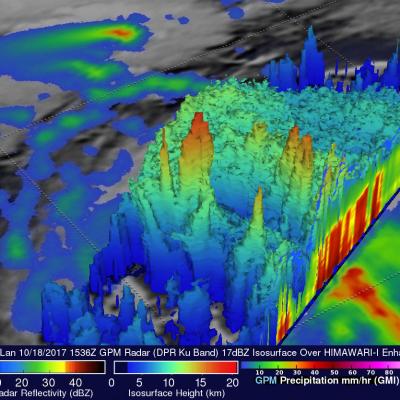
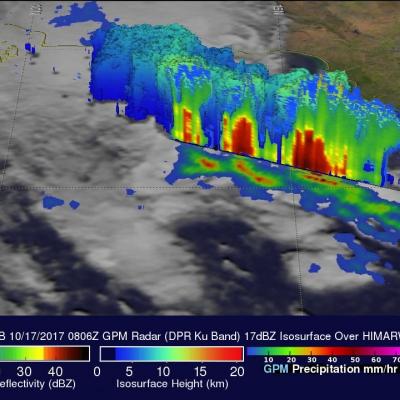
GPM Measures Tropical Storm Saola's Rainfall
The GPM core observatory had a fairly good view of tropical storm Saola on October 27, 2017 at 0243 UTC. This image shows the GPM satellite's coverage (lighter shades) of surface rainfall around tropical storm Saola. GPM's Microwave Imager (GMI) and Dual-Frequency Precipitation Radar (DPR) instruments received data showing the intensity of rainfall over the western half of tropical storm Saola. GPM's radar (DPR Ku Band) discovered that rain was falling at a rate of over 66 mm (2.6 inches) per hour in feeder bands wrapping around that side of the tropical storm. The most intense convective